Difference between revisions of "BrainRegionLAC FD HT LTN"
From aHuman Wiki
(Automated page entry using MWPush.pl) |
(Automated page entry using MWPush.pl) |
||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
* [http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s4/images/dougherty/pdougherty4_3.jpg Schematic of hypothalamic circuitry underlying satiety] - see [http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s4/chapter04.html Reference] | * [http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s4/images/dougherty/pdougherty4_3.jpg Schematic of hypothalamic circuitry underlying satiety] - see [http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s4/chapter04.html Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s4/images/dougherty/pdougherty4_3.jpg" alt="unavailable"> | + | <img src="http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s4/images/dougherty/pdougherty4_3.jpg" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;"> |
* [http://www.nature.com/nrendo/journal/v6/n8/images/nrendo.2010.93-f1.jpg Bowels control brain: gut hormones and obesity] - see [http://www.nature.com/nrendo/journal/v6/n8/fig_tab/nrendo.2010.93_F1.html Reference] | * [http://www.nature.com/nrendo/journal/v6/n8/images/nrendo.2010.93-f1.jpg Bowels control brain: gut hormones and obesity] - see [http://www.nature.com/nrendo/journal/v6/n8/fig_tab/nrendo.2010.93_F1.html Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://www.nature.com/nrendo/journal/v6/n8/images/nrendo.2010.93-f1.jpg" alt="unavailable"> | + | <img src="http://www.nature.com/nrendo/journal/v6/n8/images/nrendo.2010.93-f1.jpg" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;"> |
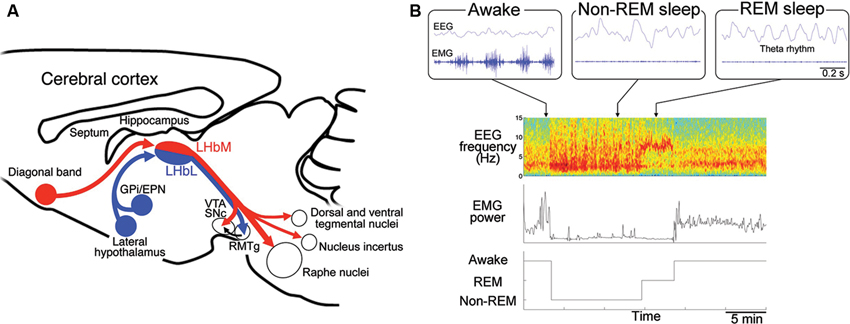
* [http://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/70852/fnhum-07-00826-HTML/image_m/fnhum-07-00826-g002.jpg Regulation of the rapid eye movement (REM) sleep by habenular projection] - see [http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fnhum.2013.00826/full Reference] | * [http://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/70852/fnhum-07-00826-HTML/image_m/fnhum-07-00826-g002.jpg Regulation of the rapid eye movement (REM) sleep by habenular projection] - see [http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fnhum.2013.00826/full Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/70852/fnhum-07-00826-HTML/image_m/fnhum-07-00826-g002.jpg" alt="unavailable"> | + | <img src="http://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/70852/fnhum-07-00826-HTML/image_m/fnhum-07-00826-g002.jpg" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;"> |
* [http://www.nature.com/neuro/journal/v17/n9/images/nn.3779-F2.jpg Both LHb and MHb control the dopaminergic and serotonergic systems] - see [http://www.nature.com/neuro/journal/v17/n9/fig_tab/nn.3779_F2.html Reference] | * [http://www.nature.com/neuro/journal/v17/n9/images/nn.3779-F2.jpg Both LHb and MHb control the dopaminergic and serotonergic systems] - see [http://www.nature.com/neuro/journal/v17/n9/fig_tab/nn.3779_F2.html Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://www.nature.com/neuro/journal/v17/n9/images/nn.3779-F2.jpg" alt="unavailable"> | + | <img src="http://www.nature.com/neuro/journal/v17/n9/images/nn.3779-F2.jpg" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;"> |
* [http://www.nature.com/npp/journal/v35/n1/images/npp2009121f1.jpg Fear regulation] - see [https://brmlab.cz/project/brain_hacking/tdcs/pfc Reference] | * [http://www.nature.com/npp/journal/v35/n1/images/npp2009121f1.jpg Fear regulation] - see [https://brmlab.cz/project/brain_hacking/tdcs/pfc Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://www.nature.com/npp/journal/v35/n1/images/npp2009121f1.jpg" alt="unavailable"> | + | <img src="http://www.nature.com/npp/journal/v35/n1/images/npp2009121f1.jpg" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;"> |
* [http://dkqlgfb5sk2dk.cloudfront.net/content/ajpregu/302/2/R215/F1.large.jpg Glucose-sensing neural network] - see [http://ajpregu.physiology.org/content/302/2/R215 Reference] | * [http://dkqlgfb5sk2dk.cloudfront.net/content/ajpregu/302/2/R215/F1.large.jpg Glucose-sensing neural network] - see [http://ajpregu.physiology.org/content/302/2/R215 Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://dkqlgfb5sk2dk.cloudfront.net/content/ajpregu/302/2/R215/F1.large.jpg" alt="unavailable"> | + | <img src="http://dkqlgfb5sk2dk.cloudfront.net/content/ajpregu/302/2/R215/F1.large.jpg" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;"> |
* [http://www.pnas.org/content/103/32/12150/F7.large.jpg Food-entrainable circadian oscillator] - see [http://www.pnas.org/content/103/32/12150/F7.expansion.html Reference] | * [http://www.pnas.org/content/103/32/12150/F7.large.jpg Food-entrainable circadian oscillator] - see [http://www.pnas.org/content/103/32/12150/F7.expansion.html Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://www.pnas.org/content/103/32/12150/F7.large.jpg" alt="unavailable"height=300> | + | <img src="http://www.pnas.org/content/103/32/12150/F7.large.jpg" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;" height=300> |
* [http://www.dana.org/uploadedImages/Images/Content_Images/SenBodyFunc2_PR2007_cont.jpg Eating and sleeping to survive] - see [http://www.dana.org/Publications/ReportDetails.aspx?id=44217 Reference] | * [http://www.dana.org/uploadedImages/Images/Content_Images/SenBodyFunc2_PR2007_cont.jpg Eating and sleeping to survive] - see [http://www.dana.org/Publications/ReportDetails.aspx?id=44217 Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://www.dana.org/uploadedImages/Images/Content_Images/SenBodyFunc2_PR2007_cont.jpg" alt="unavailable"> | + | <img src="http://www.dana.org/uploadedImages/Images/Content_Images/SenBodyFunc2_PR2007_cont.jpg" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;"> |
* [http://usvn.ahuman.org/svn/ahwiki/images/wiki/research/biomodel/intrahypothalamic.png Intrahypothalamic connections important for neural control of food intake and energy balance] - see [http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.122.2314rep=rep1type=pdf Reference] | * [http://usvn.ahuman.org/svn/ahwiki/images/wiki/research/biomodel/intrahypothalamic.png Intrahypothalamic connections important for neural control of food intake and energy balance] - see [http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.122.2314rep=rep1type=pdf Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://usvn.ahuman.org/svn/ahwiki/images/wiki/research/biomodel/intrahypothalamic.png" alt="unavailable"> | + | <img src="http://usvn.ahuman.org/svn/ahwiki/images/wiki/research/biomodel/intrahypothalamic.png" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;"> |
* [http://d2avczb82rh8fa.cloudfront.net/content/jn/107/10/2633/F1.large.jpg Connectivity map of the habenula] - see [http://jn.physiology.org/content/107/10/2633 Reference] | * [http://d2avczb82rh8fa.cloudfront.net/content/jn/107/10/2633/F1.large.jpg Connectivity map of the habenula] - see [http://jn.physiology.org/content/107/10/2633 Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://d2avczb82rh8fa.cloudfront.net/content/jn/107/10/2633/F1.large.jpg" alt="unavailable"> | + | <img src="http://d2avczb82rh8fa.cloudfront.net/content/jn/107/10/2633/F1.large.jpg" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;"> |
* [http://sni.wpengine.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/3520/SNI-3-40-g001.png Amygdala and its network] - see [http://www.surgicalneurologyint.com/article.asp?issn=2152-7806;year=2012;volume=3;issue=2;spage=40;epage=46;aulast=Langevin Reference] | * [http://sni.wpengine.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/3520/SNI-3-40-g001.png Amygdala and its network] - see [http://www.surgicalneurologyint.com/article.asp?issn=2152-7806;year=2012;volume=3;issue=2;spage=40;epage=46;aulast=Langevin Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://sni.wpengine.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/3520/SNI-3-40-g001.png" alt="unavailable"> | + | <img src="http://sni.wpengine.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/3520/SNI-3-40-g001.png" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;"> |
Revision as of 09:06, 7 September 2015
Lateral Hypothalamic Nucleus
@@Home -> BiologicalLifeResearch -> BrainAreaLAC -> BrainRegionLAC_FD_HT_LTN
This page covers biological details of component Lateral Hypothalamic Nucleus. Region is part of aHuman target integrated biological model.
- Top-down path to region: Forebrain Diencephalon -> Hypothalamus (FD.HT) -> Lateral Hypothalamic Area (LAC.FD.HT.LT) -> Lateral Hypothalamic Nucleus (LAC.FD.HT.LTN) (see Mind Maps)
- Type: nucleus
- Brain area: Lower Brain - Autonomous Control Area
- Role: relay
- Function: feeding center
- Notes to function: lesions - lack of appetite
(generated)
Components
(generated)
- no child items defined
Connectivity
(generated)
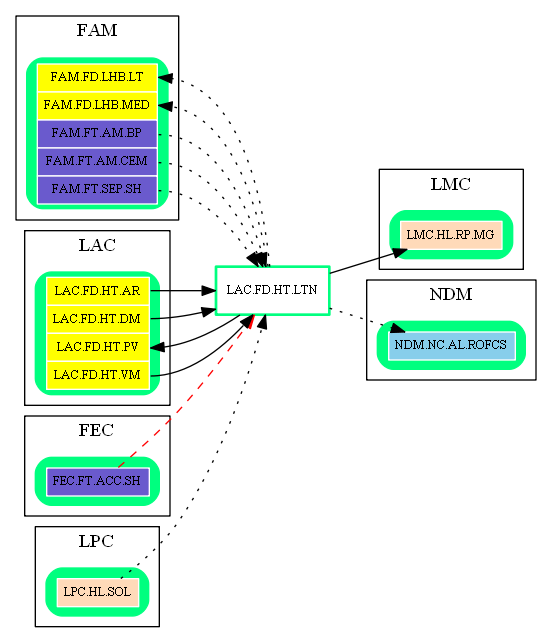
Inbound Region Connections:
| Source Area | Source Region | Source Name | Type | Reference |
| FAM | FAM.FT.AM.BP | Parvicellular Basal Amygdaloid Nucleus | excitatory-glu | Amygdala and its network (BLN -> HTS) |
| FAM.FT.AM.CEM | Medial Central Amygdaloid Nucleus | excitatory-glu | Amygdalar disruption of prefrontal cortex (AM -> HT.L, abstract) | |
| FAM.FT.SEP.SH | Septohippocampal Nucleus | excitatory-glu | Cingulate Gyrus (SEP -> HT, abstract) | |
| FEC | FEC.FT.ACC.SH | Nucleus Accumbens Shell | inhibitory-gaba | (unknown reference) |
| LAC | LAC.FD.HT.AR | Arcuate Nucleus of Hypothalamus | excitatory-glu | Intrahypothalamic connections important for neural control of food intake and energy balance (ARC -> LHA) |
| LAC.FD.HT.DM | Dorsomedial Hypothalamic Nucleus | excitatory-glu | Eating and sleeping to survive (DMH -> LHA) | |
| LAC.FD.HT.VM | Ventromedial Hypothalamic Nucleus | excitatory-glu | Glucose-sensing neural network (VMH -> LHA) | |
| LPC | LPC.HL.SOL | Solitary Nucleus | excitatory-glu | Schematic of hypothalamic circuitry underlying satiety (NTS -> LHA) |
Outbound Region Connections:
| Target Area | Target Region | Target Name | Type | Reference |
| FAM | FAM.FD.LHB.LT | Lateral Habenula Lateral Part | excitatory-glu | Regulation of the rapid eye movement (REM) sleep by habenular projection (LHT -> LHbL) |
| FAM.FD.LHB.MED | Lateral Habenula Medial Part | excitatory-glu | Both LHb and MHb control the dopaminergic and serotonergic systems (LHA -> LHbM) | |
| LAC | LAC.FD.HT.PV | Paraventricular Nucleus | excitatory-glu | Schematic of hypothalamic circuitry underlying satiety (LHA -> PVN) |
| LMC | LMC.HL.RP.MG | Raphe Magnus Nucleus | excitatory-glu | (unknown reference) |
| NDM | NDM.NC.AL.ROFCS | Sulcal Rostral Orbitofrontal Cortex | excitatory-glu | Bowels control brain: gut hormones and obesity (LHA -> OFC, abstract) |
Thirdparty Circuits
(generated)



- Fear regulation - see Reference




- Intrahypothalamic connections important for neural control of food intake and energy balance - see Reference



References
(generated)
- http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s4/chapter04.html
- http://www.nature.com/nrendo/journal/v6/n8/fig_tab/nrendo.2010.93_F1.html
- http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fnhum.2013.00826/full
- http://www.nature.com/neuro/journal/v17/n9/fig_tab/nn.3779_F2.html
- https://brmlab.cz/project/brain_hacking/tdcs/pfc
- http://ajpregu.physiology.org/content/302/2/R215
- http://www.pnas.org/content/103/32/12150/F7.expansion.html
- http://www.dana.org/Publications/ReportDetails.aspx?id=44217
- http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.122.2314rep=rep1type=pdf
- http://jn.physiology.org/content/107/10/2633
- http://www.surgicalneurologyint.com/article.asp?issn=2152-7806;year=2012;volume=3;issue=2;spage=40;epage=46;aulast=Langevin