MindTracts
From aHuman Wiki
Revision as of 15:49, 13 April 2019 by Admin (Talk | contribs) (Automated page entry using MWPush.pl)
Biological Mind Tracts
Home -> BiologicalLifeResearch -> MindTracts

This page is intended to describe set of physically existing tracts connecting set of regions across mind.
Contents
Sensory and Motor Root Neurons
(generated)
Motor Endings:
- Alpha motoneurons (MA): generate large force
- FF-type alpha motoneurons (MA-FF): fast-twitch fatigable; FIBERS={A-alpha-Ia-motor}; NERVES={abducent nerve; accessory nerve, external; accessory nerve, internal; ansa cervicalis; auricular nerve, posterior, auricular branch; auricular nerve, posterior, occipital branch; axillary nerve, anterior branch; axillary nerve, motor branch to triceps brachii; cochlear nerve; common peroneal nerve, articular branches; cutaneous nerve of foot, medial dorsal; dorsal nerve of clitoris/penis; dorsal scapular nerve; facial nerve, buccal branch; facial nerve, cervical branch; facial nerve, marginal mandibular branch; facial nerve, mouth opening muscles; facial nerve, temporal branch; facial nerve, zygomatic branch; femoral nerve, thigh, muscular branches, extensor; femoral nerve, thigh, muscular branches, flexor; fibular nerve, deep; first intercostal nerve; genitofemoral nerve, genital; glossopharyngeal nerve, stylopharyngeal branch; gluteal nerve, inferior; gluteal nerve, superior; hypoglossal nerve; inferior rectal nerve; laryngeal nerve, external; lateral pectoral nerve; long thoracic nerve; medial pectoral nerve; median nerve, motor, forearm innervation; median nerve, motor, wrist and fingers innervation; motor nerves of back, extensors; motor nerves of back, flexors; musculocutaneous nerve, motor; mylohyoid nerve; nerve of quadrate muscle of thigh; nerve to atlanto-occipital joint muscles; nerve to geniohyoid; nerve to levator scapulae; nerve to longus capitis and longus colli muscles; nerve to psoas muscles; nerve to quadratus lumborum; nerve to scalene and levator scapulae muscles; nerve to splenius capitis muscle; nerve to splenius cervilis muscle; nerve to superficial transverse perineal; nerves to coccygeus and levator ani muscles; nerves to masticatory muscles; obturator nerve; occipital nerve, greater; oculomotor nerve, inferior branch; perineal nerve, deep branch; phrenic nerve; piriform nerve; plantar nerve, lateral, deep branch; plantar nerve, lateral, superficial branch; plantar nerve, medial; radial nerve, motor; stapedius nerve; subclavian nerve; subcostal nerve, motor; suboccipital nerve; subscapular nerves; suprascapular nerve; thoracic and thoracicoabdominal intercostal nerves, flexors; thoracic intercostal nerves, extensors; thoracicoabdominal intercostal nerves, extensors; thyroid nerve; tibial nerve, muscular branches; trochlear nerve; ulnar nerve, motor, wrist and fingers innervation; vagus nerve, pharyngeal branch}
- FR-type alpha motoneurons (MA-FR): fast-twitch fatigue-resistant; FIBERS={A-alpha-Ia-motor}; NERVES={abducent nerve; accessory nerve, external; accessory nerve, internal; ansa cervicalis; auricular nerve, posterior, auricular branch; auricular nerve, posterior, occipital branch; axillary nerve, anterior branch; axillary nerve, motor branch to triceps brachii; cochlear nerve; common peroneal nerve, articular branches; cutaneous nerve of foot, medial dorsal; dorsal nerve of clitoris/penis; dorsal scapular nerve; facial nerve, buccal branch; facial nerve, cervical branch; facial nerve, marginal mandibular branch; facial nerve, mouth opening muscles; facial nerve, temporal branch; facial nerve, zygomatic branch; femoral nerve, thigh, muscular branches, extensor; femoral nerve, thigh, muscular branches, flexor; fibular nerve, deep; first intercostal nerve; genitofemoral nerve, genital; glossopharyngeal nerve, stylopharyngeal branch; gluteal nerve, inferior; gluteal nerve, superior; hypoglossal nerve; inferior rectal nerve; laryngeal nerve, external; lateral pectoral nerve; long thoracic nerve; medial pectoral nerve; median nerve, motor, forearm innervation; median nerve, motor, wrist and fingers innervation; motor nerves of back, extensors; motor nerves of back, flexors; musculocutaneous nerve, motor; mylohyoid nerve; nerve of quadrate muscle of thigh; nerve to atlanto-occipital joint muscles; nerve to geniohyoid; nerve to levator scapulae; nerve to longus capitis and longus colli muscles; nerve to psoas muscles; nerve to quadratus lumborum; nerve to scalene and levator scapulae muscles; nerve to splenius capitis muscle; nerve to splenius cervilis muscle; nerve to superficial transverse perineal; nerves to coccygeus and levator ani muscles; nerves to masticatory muscles; obturator nerve; occipital nerve, greater; oculomotor nerve, inferior branch; perineal nerve, deep branch; phrenic nerve; piriform nerve; plantar nerve, lateral, deep branch; plantar nerve, lateral, superficial branch; plantar nerve, medial; radial nerve, motor; stapedius nerve; subclavian nerve; subcostal nerve, motor; suboccipital nerve; subscapular nerves; suprascapular nerve; thoracic and thoracicoabdominal intercostal nerves, flexors; thoracic intercostal nerves, extensors; thoracicoabdominal intercostal nerves, extensors; thyroid nerve; tibial nerve, muscular branches; trochlear nerve; ulnar nerve, motor, wrist and fingers innervation; vagus nerve, pharyngeal branch}
- S-type alpha motoneurons (MA-S): slow-twitch fatigue-resistant; FIBERS={A-alpha-Ia-motor}; NERVES={abducent nerve; accessory nerve, external; accessory nerve, internal; ansa cervicalis; auricular nerve, posterior, auricular branch; auricular nerve, posterior, occipital branch; axillary nerve, anterior branch; axillary nerve, motor branch to triceps brachii; cochlear nerve; common peroneal nerve, articular branches; cutaneous nerve of foot, medial dorsal; dorsal nerve of clitoris/penis; dorsal scapular nerve; facial nerve, buccal branch; facial nerve, cervical branch; facial nerve, marginal mandibular branch; facial nerve, mouth opening muscles; facial nerve, temporal branch; facial nerve, zygomatic branch; femoral nerve, thigh, muscular branches, extensor; femoral nerve, thigh, muscular branches, flexor; fibular nerve, deep; first intercostal nerve; genitofemoral nerve, genital; glossopharyngeal nerve, stylopharyngeal branch; gluteal nerve, inferior; gluteal nerve, superior; hypoglossal nerve; inferior rectal nerve; laryngeal nerve, external; lateral pectoral nerve; long thoracic nerve; medial pectoral nerve; median nerve, motor, forearm innervation; median nerve, motor, wrist and fingers innervation; motor nerves of back, extensors; motor nerves of back, flexors; musculocutaneous nerve, motor; mylohyoid nerve; nerve of quadrate muscle of thigh; nerve to atlanto-occipital joint muscles; nerve to geniohyoid; nerve to levator scapulae; nerve to longus capitis and longus colli muscles; nerve to psoas muscles; nerve to quadratus lumborum; nerve to scalene and levator scapulae muscles; nerve to splenius capitis muscle; nerve to splenius cervilis muscle; nerve to superficial transverse perineal; nerves to coccygeus and levator ani muscles; nerves to masticatory muscles; obturator nerve; occipital nerve, greater; oculomotor nerve, inferior branch; perineal nerve, deep branch; phrenic nerve; piriform nerve; plantar nerve, lateral, deep branch; plantar nerve, lateral, superficial branch; plantar nerve, medial; radial nerve, motor; stapedius nerve; subclavian nerve; subcostal nerve, motor; suboccipital nerve; subscapular nerves; suprascapular nerve; thoracic and thoracicoabdominal intercostal nerves, flexors; thoracic intercostal nerves, extensors; thoracicoabdominal intercostal nerves, extensors; thyroid nerve; tibial nerve, muscular branches; trochlear nerve; ulnar nerve, motor, wrist and fingers innervation; vagus nerve, pharyngeal branch}
- Beta motoneurons (MB): affect both extrafusal and intrafusal muscle fibers
- beta dynamic motoneurons (MB-D): slow contracting motor units; FIBERS={A-beta-motor}
- beta static motoneurons (MB-S): fast contracting motor units; FIBERS={A-beta-motor}
- Gamma motoneurons (MG): enforce alpha motoneurons
- gamma dynamic motoneurons (MG-D): contract muscle spindles from both ends; FIBERS={A-gamma-motor}
- gamma static motoneurons (MG-S): contract muscle spindles from both ends; FIBERS={A-gamma-motor}
- postganglionic autonomic motoneurons (MPG): postganglionic autonomic
- postganglionic parasympathetic motoneurons (MPG-P): visceral activity and repose, short, local; FIBERS={C-motor}
- postganglionic sympathetic motoneurons (MPG-S): muscles and skin, pre/post - temporal summation and spatial summation; FIBERS={C-motor}
- preganglionic autonomic motoneurons (MPA): preganglionic paravertebral/prevertebral sympathetic, spinal/cranial parasympathetic
- preganglionic parasympathetic cranial (MPA-PC): cranial nerves III, VII, IX and X long fibers to parasympathetic ganglia; FIBERS={B-motor}; NERVES={auriculotemporal nerve, parotid branch; chorda tympani, parasympathetic; inferior laryngeal nerve; nasopalatine nerve, parasympathetic fibers; oculomotor nerve, superior branch; palatine nerves, parasympathetic fibers; petrosal nerve, greater, to lacrimal gland; pharyngeal nerve; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, nipple; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, to penis/clitoris; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, to rectum; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, to stomach; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, to urinary bladder; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, uterovaginal; sublingual nerve; tympanic nerve; vagus nerve, bronchial branch; vagus nerve, cardiac branch; vagus nerve, esophageal branches; vagus nerve, gastric branch; vagus nerve, gastroduodenal branch; vagus nerve, hepatic branch proper; vagus nerve, spleen, kidney, small intestine and colon}
- preganglionic parasympathetic spinal (MPA-PS): spinal cord long fibers to parasympathetic ganglia; FIBERS={B-motor}
- preganglionic paravertebral sympathetic (MPA-SPAV): short to paravertebral sympathetic ganglia; FIBERS={B-motor}; NERVES={ansa subclavia; caroticotympanic nerves; cervical cardiac nerve, inferior, sympathetic; cervical cardiac nerve, middle, sympathetic; ciliary nerves, sympathetic fibers; external carotid nerve; genitofemoral nerve, genital branch; greater thoracic splanchnic nerve; internal carotid nerve, to tarsal muscle; jugular nerve, sympathetic; left hypogastric nerve, cervical; left hypogastric nerve, lubricate; left hypogastric nerve, prostatic; left hypogastric nerve, ureteric; left hypogastric nerve, uterovaginal; lesser splanchnic nerve; lowest splanchnic nerve; middle cervical ganglion, sympathetic fibers, grey communicating rami; middle cervical ganglion, thyroid branches; right hypogastric nerve; scrotal nerve, posterior; stellate ganglion, arterial branches; stellate ganglion, sympathetic fibers, grey communicating rami; superior cervical cardiac nerve; superior cervical ganglion, laryngopharyngeal branches; superior cervical ganglion, sympathetic fibers, grey communicating rami; thoracic sympatetic chain ganglia}
- preganglionic prevertebral sympathetic (MPA-SPRV): long to prevertebral sympathetic ganglia; FIBERS={B-motor}; NERVES={palatine nerve, sympathetic fibers}
Sensory Endings:
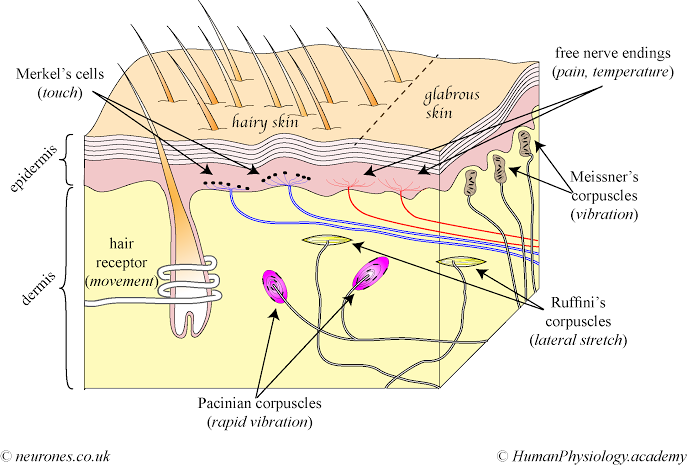
- Mechanoreceptors (SMECH)
- Deep tissue mechanoreceptors (SMECH-DEEP)
- Pacinian corpuscles (SPC): responds to vibration; vibration 60-400 Hz, deep; FIBERS={A-beta-sensory; A-delta-sensory}; NERVES={Genitalia nerves, somatic; Rectum nerves, somatic; alveolar nerves, superior, anterior and middle branches; alveolar nerves, superior, posterior branch; arm nerves, sensory; auricular nerve, posterior, auricular branch; auricular nerves, anterior; auriculotemporal nerve, branch to tympanic membrane; auriculotemporal nerve, branches communicating with facial nerve; buccal nerve; cervical nerve, transverse; ciliary nerves, sensory fibers; ethmoidal nerve; frontal nerve; glossopharyngeal nerve, lingual branch; glossopharyngeal nerve, meningeal branches; great auricular nerve, anterior branch; great auricular nerve, posterior branch; inferior alveolar nerve, dental branches; inferior alveolar nerve, gingival branches; infraorbital nerve, external nasal branch; infraorbital nerve, inferior palpebral branch; infratrochlear nerve; internal nasal nerve; jugular nerve, sensory; lacrimal nerve; lingual nerve, branch to isthmus of fauces; lingual nerve, lingual branch; mandibular nerve, meningeal branch; maxillary nerve, meningeal branch; mental nerve; nasopalatine nerve, sensory fibers; nerve of external acoustic meatus; occipital nerve, neck; occipital nerve, third; palatine nerve, sensory fibers; shoulder nerves, mixed; sublingual nerve; superior labial branch; supraclavicular nerves, intermediate; supraclavicular nerves, lateral; supraclavicular nerves, medial; tentorial nerve; vagus nerve, auricular branch; vagus nerve, meningeal branch; zygomatic nerve}
- Ruffini corpuscles (SRC): responds to pressure on skin; stretching of skin, crude touch; FIBERS={A-alpha-Ib-sensory; A-beta-sensory}; NERVES={Genitalia nerves, somatic; Rectum nerves, somatic; alveolar nerves, superior, anterior and middle branches; alveolar nerves, superior, posterior branch; arm nerves, sensory; auricular nerve, posterior, auricular branch; auricular nerves, anterior; auriculotemporal nerve, branch to tympanic membrane; auriculotemporal nerve, branches communicating with facial nerve; buccal nerve; cervical nerve, transverse; ciliary nerves, sensory fibers; ethmoidal nerve; frontal nerve; glossopharyngeal nerve, lingual branch; glossopharyngeal nerve, meningeal branches; great auricular nerve, anterior branch; great auricular nerve, posterior branch; inferior alveolar nerve, dental branches; inferior alveolar nerve, gingival branches; infraorbital nerve, external nasal branch; infraorbital nerve, inferior palpebral branch; infratrochlear nerve; internal nasal nerve; jugular nerve, sensory; lacrimal nerve; lingual nerve, branch to isthmus of fauces; lingual nerve, lingual branch; mandibular nerve, meningeal branch; maxillary nerve, meningeal branch; mental nerve; nasopalatine nerve, sensory fibers; nerve of external acoustic meatus; occipital nerve, neck; occipital nerve, third; palatine nerve, sensory fibers; shoulder nerves, mixed; sublingual nerve; superior labial branch; supraclavicular nerves, intermediate; supraclavicular nerves, lateral; supraclavicular nerves, medial; tentorial nerve; vagus nerve, auricular branch; vagus nerve, meningeal branch; zygomatic nerve}
- Skin mechanoreceptors (SMECH-SKIN)
- Hair follicle receptors (SHF): responds to hair displacement; touch, hairy skin velocity; FIBERS={A-beta-sensory}; NERVES={Genitalia nerves, somatic; Rectum nerves, somatic; alveolar nerves, superior, anterior and middle branches; alveolar nerves, superior, posterior branch; arm nerves, sensory; auricular nerve, posterior, auricular branch; auricular nerves, anterior; auriculotemporal nerve, branch to tympanic membrane; auriculotemporal nerve, branches communicating with facial nerve; buccal nerve; cervical nerve, transverse; ciliary nerves, sensory fibers; ethmoidal nerve; frontal nerve; glossopharyngeal nerve, lingual branch; glossopharyngeal nerve, meningeal branches; great auricular nerve, anterior branch; great auricular nerve, posterior branch; inferior alveolar nerve, dental branches; inferior alveolar nerve, gingival branches; infraorbital nerve, external nasal branch; infraorbital nerve, inferior palpebral branch; infratrochlear nerve; internal nasal nerve; jugular nerve, sensory; lacrimal nerve; lingual nerve, branch to isthmus of fauces; lingual nerve, lingual branch; mandibular nerve, meningeal branch; maxillary nerve, meningeal branch; mental nerve; nasopalatine nerve, sensory fibers; nerve of external acoustic meatus; occipital nerve, neck; occipital nerve, third; palatine nerve, sensory fibers; shoulder nerves, mixed; sublingual nerve; superior labial branch; supraclavicular nerves, intermediate; supraclavicular nerves, lateral; supraclavicular nerves, medial; tentorial nerve; vagus nerve, auricular branch; vagus nerve, meningeal branch; zygomatic nerve}
- Meissner corpuscles (SMC): responds to vibration; vibration 20-50 Hz; dynamic touch/pressure; FIBERS={A-alpha-Ia-sensory; A-beta-sensory}; NERVES={Genitalia nerves, somatic; Rectum nerves, somatic; alveolar nerves, superior, anterior and middle branches; alveolar nerves, superior, posterior branch; arm nerves, sensory; auricular nerve, posterior, auricular branch; auricular nerves, anterior; auriculotemporal nerve, branch to tympanic membrane; auriculotemporal nerve, branches communicating with facial nerve; buccal nerve; cervical nerve, transverse; ciliary nerves, sensory fibers; ethmoidal nerve; frontal nerve; glossopharyngeal nerve, lingual branch; glossopharyngeal nerve, meningeal branches; great auricular nerve, anterior branch; great auricular nerve, posterior branch; inferior alveolar nerve, dental branches; inferior alveolar nerve, gingival branches; infraorbital nerve, external nasal branch; infraorbital nerve, inferior palpebral branch; infratrochlear nerve; internal nasal nerve; jugular nerve, sensory; lacrimal nerve; lingual nerve, branch to isthmus of fauces; lingual nerve, lingual branch; mandibular nerve, meningeal branch; maxillary nerve, meningeal branch; mental nerve; nasopalatine nerve, sensory fibers; nerve of external acoustic meatus; occipital nerve, neck; occipital nerve, third; palatine nerve, sensory fibers; shoulder nerves, mixed; sublingual nerve; superior labial branch; supraclavicular nerves, intermediate; supraclavicular nerves, lateral; supraclavicular nerves, medial; tentorial nerve; vagus nerve, auricular branch; vagus nerve, meningeal branch; zygomatic nerve}
- Merkel disk receptors (SMD): responds to pressure on skin; vibration 5-15 Hz, static (sustained) touch/pressure; FIBERS={A-beta-sensory}; NERVES={Genitalia nerves, somatic; Rectum nerves, somatic; alveolar nerves, superior, anterior and middle branches; alveolar nerves, superior, posterior branch; arm nerves, sensory; auricular nerve, posterior, auricular branch; auricular nerves, anterior; auriculotemporal nerve, branch to tympanic membrane; auriculotemporal nerve, branches communicating with facial nerve; buccal nerve; cervical nerve, transverse; ciliary nerves, sensory fibers; ethmoidal nerve; frontal nerve; glossopharyngeal nerve, lingual branch; glossopharyngeal nerve, meningeal branches; great auricular nerve, anterior branch; great auricular nerve, posterior branch; inferior alveolar nerve, dental branches; inferior alveolar nerve, gingival branches; infraorbital nerve, external nasal branch; infraorbital nerve, inferior palpebral branch; infratrochlear nerve; internal nasal nerve; jugular nerve, sensory; lacrimal nerve; lingual nerve, branch to isthmus of fauces; lingual nerve, lingual branch; mandibular nerve, meningeal branch; maxillary nerve, meningeal branch; mental nerve; nasopalatine nerve, sensory fibers; nerve of external acoustic meatus; occipital nerve, neck; occipital nerve, third; palatine nerve, sensory fibers; shoulder nerves, mixed; sublingual nerve; superior labial branch; supraclavicular nerves, intermediate; supraclavicular nerves, lateral; supraclavicular nerves, medial; tentorial nerve; vagus nerve, auricular branch; vagus nerve, meningeal branch; zygomatic nerve}
- Deep tissue mechanoreceptors (SMECH-DEEP)
- Pain and temperature receptors (SPT)
- A-delta fiber nociceptors (SAD): fast/first pain information; FIBERS={A-delta-sensory}; NERVES={Genitalia nerves, somatic; Rectum nerves, somatic; arm nerves, sensory; cervical cardiac nerve, sensory; cluneal nerves; coccygeal plexus; cutaneous nerve of thigh, lateral; femoral nerve, leg; femoral nerve, thigh, sensory; genitofemoral nerve, thigh; gluteal nerve, superior; greater thoracic splanchnic nerve; intercostal muscular somatic nerves; intercostal nerves, anterior cutaneous branches; intercostal nerves, posterior lateral cutaneous branches; intercostobrachial nerve; left hypogastric nerve, cervical; left hypogastric nerve, lubricate; left hypogastric nerve, prostatic; left hypogastric nerve, ureteric; left hypogastric nerve, uterovaginal; lesser splanchnic nerve; lowest splanchnic nerve; nerve of quadrate muscle of thigh; nerves to masticatory muscles; obturator nerve; phrenic nerve; right hypogastric nerve; sciatic nerve; sciatic nerves, second; shoulder nerves, mixed; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, nipple; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, to penis/clitoris; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, to rectum; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, to stomach; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, to urinary bladder; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, uterovaginal; subcostal nerve, sensory; thoracic breast nerves; vagus nerve, bronchial branch; vagus nerve, cardiac branch; vagus nerve, esophageal branches; vagus nerve, gastric branch; vagus nerve, gastroduodenal branch; vagus nerve, hepatic branch proper; vagus nerve, spleen, kidney, small intestine and colon}
- Cold receptors (SCR): respond to low temperature; FIBERS={A-delta-sensory}; NERVES={nerves to masticatory muscles}
- Nonencapsulated free-nerve endings (SFN): pain and temperature
- C fiber nociceptors (SFN-CN): responsible for the second, burning pain; FIBERS={C-sensory}; NERVES={Genitalia nerves, somatic; Rectum nerves, somatic; arm nerves, sensory; cluneal nerves; coccygeal plexus; cutaneous nerve of thigh, lateral; femoral nerve, leg; femoral nerve, thigh, sensory; genitofemoral nerve, thigh; gluteal nerve, superior; intercostal muscular somatic nerves; intercostal nerves, anterior cutaneous branches; intercostal nerves, posterior lateral cutaneous branches; intercostobrachial nerve; lacrimal nerve; laryngeal nerve, internal; nerve of quadrate muscle of thigh; nerves to masticatory muscles; obturator nerve; recurrent laryngeal nerve, posterior; sciatic nerve; sciatic nerves, second; shoulder nerves, mixed; subcostal nerve, sensory; thoracic breast nerves; tympanic nerve}
- C fiber warming-specific receptors (SFN-CW): responsible for warmth; FIBERS={C-sensory}; NERVES={Genitalia nerves, somatic; Rectum nerves, somatic; arm nerves, sensory; cluneal nerves; coccygeal plexus; cutaneous nerve of thigh, lateral; femoral nerve, leg; femoral nerve, thigh, sensory; genitofemoral nerve, thigh; gluteal nerve, superior; intercostal muscular somatic nerves; intercostal nerves, anterior cutaneous branches; intercostal nerves, posterior lateral cutaneous branches; intercostobrachial nerve; lacrimal nerve; laryngeal nerve, internal; nerve of quadrate muscle of thigh; nerves to masticatory muscles; obturator nerve; recurrent laryngeal nerve, posterior; sciatic nerve; sciatic nerves, second; shoulder nerves, mixed; subcostal nerve, sensory; thoracic breast nerves; tympanic nerve}
- C mechano- and metabo- receptors in muscles or joints (SFN-CM): responsible for muscle exercise, burn and cramp; FIBERS={C-sensory}; NERVES={Genitalia nerves, somatic; Rectum nerves, somatic; arm nerves, sensory; cluneal nerves; coccygeal plexus; cutaneous nerve of thigh, lateral; femoral nerve, leg; femoral nerve, thigh, sensory; genitofemoral nerve, thigh; gluteal nerve, superior; intercostal muscular somatic nerves; intercostal nerves, anterior cutaneous branches; intercostal nerves, posterior lateral cutaneous branches; intercostobrachial nerve; lacrimal nerve; laryngeal nerve, internal; nerve of quadrate muscle of thigh; nerves to masticatory muscles; obturator nerve; recurrent laryngeal nerve, posterior; sciatic nerve; sciatic nerves, second; shoulder nerves, mixed; subcostal nerve, sensory; thoracic breast nerves; tympanic nerve}
- tactile C fibers (SFN-CT): sensual touch; FIBERS={C-sensory}; NERVES={Genitalia nerves, somatic; Rectum nerves, somatic; arm nerves, sensory; cluneal nerves; coccygeal plexus; cutaneous nerve of thigh, lateral; femoral nerve, leg; femoral nerve, thigh, sensory; genitofemoral nerve, thigh; gluteal nerve, superior; intercostal muscular somatic nerves; intercostal nerves, anterior cutaneous branches; intercostal nerves, posterior lateral cutaneous branches; intercostobrachial nerve; lacrimal nerve; laryngeal nerve, internal; nerve of quadrate muscle of thigh; nerves to masticatory muscles; obturator nerve; recurrent laryngeal nerve, posterior; sciatic nerve; sciatic nerves, second; shoulder nerves, mixed; subcostal nerve, sensory; thoracic breast nerves; tympanic nerve}
- ultra-slow histamine-selective C fibers (SFN-CI): responsible for itch; FIBERS={C-sensory}; NERVES={Genitalia nerves, somatic; Rectum nerves, somatic; arm nerves, sensory; cluneal nerves; coccygeal plexus; cutaneous nerve of thigh, lateral; femoral nerve, leg; femoral nerve, thigh, sensory; genitofemoral nerve, thigh; gluteal nerve, superior; intercostal muscular somatic nerves; intercostal nerves, anterior cutaneous branches; intercostal nerves, posterior lateral cutaneous branches; intercostobrachial nerve; lacrimal nerve; laryngeal nerve, internal; nerve of quadrate muscle of thigh; nerves to masticatory muscles; obturator nerve; recurrent laryngeal nerve, posterior; sciatic nerve; sciatic nerves, second; shoulder nerves, mixed; subcostal nerve, sensory; thoracic breast nerves; tympanic nerve}
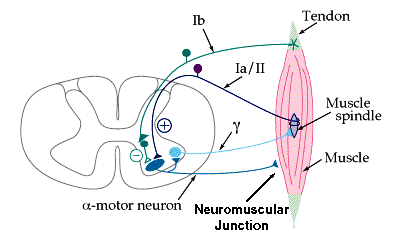
- Proprioceptors (SPROP)
- Golgi tendon organs (SGT): muscle tension; FIBERS={A-alpha-Ib-sensory}; NERVES={musculocutaneous nerve, sensory; occipital nerve, third; suboccipital nerve}
- Muscle spindles (SMS): skeletal muscle, stretch by muscle length, fast
- Dynamic nuclear bag fibers (SMS-DN): report rate of change of muscle length; FIBERS={A-alpha-Ib-sensory}; NERVES={musculocutaneous nerve, sensory; occipital nerve, third; suboccipital nerve}
- Nuclear chain fibers (SMS-NC): report static length of muscle; FIBERS={A-alpha-Ib-sensory}; NERVES={musculocutaneous nerve, sensory; occipital nerve, third; suboccipital nerve}
- Static nuclear bag fibers (SMS-SN): report static length of muscle; FIBERS={A-alpha-Ib-sensory}; NERVES={musculocutaneous nerve, sensory; occipital nerve, third; suboccipital nerve}
- Special Senses (SPS)
- Baroreceptors (SSB): blood pressure in carotid sinus; FIBERS={C-sensory}; NERVES={Hering's nerve}
- Cochlea receptor (SSA): audition; FIBERS={A-delta-sensory}; NERVES={cochlear nerve}
- Olfactory receptor (SSS): smell, odor detection; FIBERS={C-sensory}; NERVES={olfactory nerves}
- Oxigen chemoreceptors (SSO): oxigen level in carotid body; FIBERS={C-sensory}; NERVES={Hering's nerve}
- Retinal rods and cones (SSV): vision receptors; FIBERS={A-delta-sensory; C-sensory}; NERVES={ampullar nerve; optic nerve; saccular nerve; utricular nerve}
- Taste buds (SST): taste receptors; FIBERS={C-sensory}; NERVES={communicating branch of chorda tympani with lingual nerve; glossopharyngeal nerve, tonsillar branch; palatine nerves, lesser, parasympathetic fibers}
Fibers by thickness:
A-alpha* (mixed, 12-22 mcm, 70-120 m/sec): low theshold, 2ms after stimulus (type Ia,Ib; motoneurons, touch, position and velocity)
- A-alpha-Ia (mixed)
- A-alpha-Ia-motor - alpha motoneurons (motor); ENDINGS={MA-FF,MA-FR,MA-S}; NERVES={abducent nerve; accessory nerve, external; accessory nerve, internal; ansa cervicalis; auricular nerve, posterior, auricular branch; auricular nerve, posterior, occipital branch; axillary nerve, anterior branch; axillary nerve, motor branch to triceps brachii; cochlear nerve; common peroneal nerve, articular branches; cutaneous nerve of foot, medial dorsal; dorsal nerve of clitoris/penis; dorsal scapular nerve; facial nerve, buccal branch; facial nerve, cervical branch; facial nerve, marginal mandibular branch; facial nerve, mouth opening muscles; facial nerve, temporal branch; facial nerve, zygomatic branch; femoral nerve, thigh, muscular branches, extensor; femoral nerve, thigh, muscular branches, flexor; fibular nerve, deep; first intercostal nerve; genitofemoral nerve, genital; glossopharyngeal nerve, stylopharyngeal branch; gluteal nerve, inferior; gluteal nerve, superior; hypoglossal nerve; inferior rectal nerve; laryngeal nerve, external; lateral pectoral nerve; long thoracic nerve; medial pectoral nerve; median nerve, motor, forearm innervation; median nerve, motor, wrist and fingers innervation; motor nerves of back, extensors; motor nerves of back, flexors; musculocutaneous nerve, motor; mylohyoid nerve; nerve of quadrate muscle of thigh; nerve to atlanto-occipital joint muscles; nerve to geniohyoid; nerve to levator scapulae; nerve to longus capitis and longus colli muscles; nerve to psoas muscles; nerve to quadratus lumborum; nerve to scalene and levator scapulae muscles; nerve to splenius capitis muscle; nerve to splenius cervilis muscle; nerve to superficial transverse perineal; nerves to coccygeus and levator ani muscles; nerves to masticatory muscles; obturator nerve; occipital nerve, greater; oculomotor nerve, inferior branch; perineal nerve, deep branch; phrenic nerve; piriform nerve; plantar nerve, lateral, deep branch; plantar nerve, lateral, superficial branch; plantar nerve, medial; radial nerve, motor; stapedius nerve; subclavian nerve; subcostal nerve, motor; suboccipital nerve; subscapular nerves; suprascapular nerve; thoracic and thoracicoabdominal intercostal nerves, flexors; thoracic intercostal nerves, extensors; thoracicoabdominal intercostal nerves, extensors; thyroid nerve; tibial nerve, muscular branches; trochlear nerve; ulnar nerve, motor, wrist and fingers innervation; vagus nerve, pharyngeal branch}
- A-alpha-Ia-sensory (sensory): skin, two-point discrimination (muscle spindle primary sensory endings; extrafusal muscles, Meissner's corpuscles; annulospiral endings, length and velocity); ENDINGS={SMC}
- A-alpha-Ib-sensory (sensory): report load being applied to muscle, stretching of skin; ENDINGS={SGT,SRC,SMS-NC,SMS-SN,SMS-DN}; NERVES={musculocutaneous nerve, sensory; occipital nerve, third; suboccipital nerve}
A-beta* (mixed, 8-13 mcm, 40-70 m/sec): higher theshold, 4ms after stimulus (type II; fine touch, kinesthesia, muscle spindle secondary endings)
- A-beta-motor - beta motoneurons (motor): skeleto-fusimotor, intrafusal fibers and collaterals to extrafusal muscle fibers, muscle spindles, increase dynamic sensitivity of ending; ENDINGS={MB-D,MB-S}
- A-beta-sensory (sensory): fine touch, kinesthesia (length only; secondary afferents, flower spray endings); ENDINGS={SMD,SRC,SHF,SPC,SMC}; NERVES={Genitalia nerves, somatic; Rectum nerves, somatic; alveolar nerves, superior, anterior and middle branches; alveolar nerves, superior, posterior branch; arm nerves, sensory; auricular nerve, posterior, auricular branch; auricular nerves, anterior; auriculotemporal nerve, branch to tympanic membrane; auriculotemporal nerve, branches communicating with facial nerve; buccal nerve; cervical nerve, transverse; ciliary nerves, sensory fibers; ethmoidal nerve; frontal nerve; glossopharyngeal nerve, lingual branch; glossopharyngeal nerve, meningeal branches; great auricular nerve, anterior branch; great auricular nerve, posterior branch; inferior alveolar nerve, dental branches; inferior alveolar nerve, gingival branches; infraorbital nerve, external nasal branch; infraorbital nerve, inferior palpebral branch; infratrochlear nerve; internal nasal nerve; jugular nerve, sensory; lacrimal nerve; lingual nerve, branch to isthmus of fauces; lingual nerve, lingual branch; mandibular nerve, meningeal branch; maxillary nerve, meningeal branch; mental nerve; nasopalatine nerve, sensory fibers; nerve of external acoustic meatus; occipital nerve, neck; occipital nerve, third; palatine nerve, sensory fibers; shoulder nerves, mixed; sublingual nerve; superior labial branch; supraclavicular nerves, intermediate; supraclavicular nerves, lateral; supraclavicular nerves, medial; tentorial nerve; vagus nerve, auricular branch; vagus nerve, meningeal branch; zygomatic nerve}
A-delta-sensory* (sensory, 1-4 mcm, 5-15 m/sec): noxious, cold, pressure; 20ms after stimulus (type III; thinly-myelinated; noxious receptors - first/fast, sharp, well-localized pain; cold receptors - temperature, high-threshold mechano/heat, phasic; pressure - rapidly adapting mechanosensitive, directional selectivity, crude touch; auditory axons 2 mcm; vestibular axons 3 mcm); ENDINGS={SAD,SCR,SPC,SSA,SSV}; NERVES={Genitalia nerves, somatic; Rectum nerves, somatic; ampullar nerve; arm nerves, sensory; cervical cardiac nerve, sensory; cluneal nerves; coccygeal plexus; cochlear nerve; cutaneous nerve of thigh, lateral; femoral nerve, leg; femoral nerve, thigh, sensory; genitofemoral nerve, thigh; gluteal nerve, superior; greater thoracic splanchnic nerve; intercostal muscular somatic nerves; intercostal nerves, anterior cutaneous branches; intercostal nerves, posterior lateral cutaneous branches; intercostobrachial nerve; left hypogastric nerve, cervical; left hypogastric nerve, lubricate; left hypogastric nerve, prostatic; left hypogastric nerve, ureteric; left hypogastric nerve, uterovaginal; lesser splanchnic nerve; lowest splanchnic nerve; nerve of quadrate muscle of thigh; nerves to masticatory muscles; obturator nerve; phrenic nerve; right hypogastric nerve; saccular nerve; sciatic nerve; sciatic nerves, second; shoulder nerves, mixed; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, nipple; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, to penis/clitoris; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, to rectum; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, to stomach; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, to urinary bladder; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, uterovaginal; subcostal nerve, sensory; thoracic breast nerves; utricular nerve; vagus nerve, bronchial branch; vagus nerve, cardiac branch; vagus nerve, esophageal branches; vagus nerve, gastric branch; vagus nerve, gastroduodenal branch; vagus nerve, hepatic branch proper; vagus nerve, spleen, kidney, small intestine and colon}
A-gamma-motor* (motor, 4-8 mcm, 15-40 m/sec): intrafusal muscle fibers, 6ms after stimulus (skeletal muscle tone, contract muscle spindles from both ends, fusimotor gamma neurons, affect Ia/II); ENDINGS={MG-D,MG-S}
B-motor* (motor, 1-3 mcm, 3-14 m/sec): preganglionic autonomic (myelinated, ACh, sympathetic only in T1-L3, IML); ENDINGS={MPA-SPAV,MPA-SPRV,MPA-PS,MPA-PC}; NERVES={ansa subclavia; auriculotemporal nerve, parotid branch; caroticotympanic nerves; cervical cardiac nerve, inferior, sympathetic; cervical cardiac nerve, middle, sympathetic; chorda tympani, parasympathetic; ciliary nerves, sympathetic fibers; external carotid nerve; genitofemoral nerve, genital branch; greater thoracic splanchnic nerve; inferior laryngeal nerve; internal carotid nerve, to tarsal muscle; jugular nerve, sympathetic; left hypogastric nerve, cervical; left hypogastric nerve, lubricate; left hypogastric nerve, prostatic; left hypogastric nerve, ureteric; left hypogastric nerve, uterovaginal; lesser splanchnic nerve; lowest splanchnic nerve; middle cervical ganglion, sympathetic fibers, grey communicating rami; middle cervical ganglion, thyroid branches; nasopalatine nerve, parasympathetic fibers; oculomotor nerve, superior branch; palatine nerve, sympathetic fibers; palatine nerves, parasympathetic fibers; petrosal nerve, greater, to lacrimal gland; pharyngeal nerve; right hypogastric nerve; scrotal nerve, posterior; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, nipple; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, to penis/clitoris; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, to rectum; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, to stomach; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, to urinary bladder; splanchnic nerves, pelvic, uterovaginal; stellate ganglion, arterial branches; stellate ganglion, sympathetic fibers, grey communicating rami; sublingual nerve; superior cervical cardiac nerve; superior cervical ganglion, laryngopharyngeal branches; superior cervical ganglion, sympathetic fibers, grey communicating rami; thoracic sympatetic chain ganglia; tympanic nerve; vagus nerve, bronchial branch; vagus nerve, cardiac branch; vagus nerve, esophageal branches; vagus nerve, gastric branch; vagus nerve, gastroduodenal branch; vagus nerve, hepatic branch proper; vagus nerve, spleen, kidney, small intestine and colon}
C* (mixed, 0.1-1 mcm, 0.2-2 m/sec): pain, touch, pressure, temperature, postganglionic autonomic, taste (60ms after stimulus)
- C-motor (motor): postganglionic autonomic; ENDINGS={MPG-S,MPG-P}
- C-sensory (sensory): pain and temperature, special (optic axons width average 0.72 mcm; olfactory axons 0.35 mcm); ENDINGS={SFN-CN,SFN-CW,SFN-CI,SFN-CT,SFN-CM,SST,SSV,SSO,SSB,SSS}; NERVES={Genitalia nerves, somatic; Hering's nerve; Rectum nerves, somatic; arm nerves, sensory; cluneal nerves; coccygeal plexus; communicating branch of chorda tympani with lingual nerve; cutaneous nerve of thigh, lateral; femoral nerve, leg; femoral nerve, thigh, sensory; genitofemoral nerve, thigh; glossopharyngeal nerve, tonsillar branch; gluteal nerve, superior; intercostal muscular somatic nerves; intercostal nerves, anterior cutaneous branches; intercostal nerves, posterior lateral cutaneous branches; intercostobrachial nerve; lacrimal nerve; laryngeal nerve, internal; nerve of quadrate muscle of thigh; nerves to masticatory muscles; obturator nerve; olfactory nerves; optic nerve; palatine nerves, lesser, parasympathetic fibers; recurrent laryngeal nerve, posterior; sciatic nerve; sciatic nerves, second; shoulder nerves, mixed; subcostal nerve, sensory; thoracic breast nerves; tympanic nerve}
Tracts Hierarchy
(generated)
Ascending Tracts
TRACT SET: Ascending Tracts
- TRACT ALS: anterolateral system - pain transfer
- TRACT SLS: spinolimbic system - autonomic body pain transfer
- TRACT SHTT: spinohypothalamic tract - autonomic body pain transfer to hypothalamus
- TRACT SMST: spinomesencephalic tract - descending modulation of pain
- TRACT SST: spinosolitary tract - autonomic body pain transfer to parabrachial nucleus
- TRACT SRS: spinoreticular system - automatic body pain reflection
- TRACT SMRT: spinomedulloreticular tract - automatic body pain spinal reflection
- TRACT SPRT: spinopontoreticular tract - automatic body pain cortical reflection
- TRACT STCT: spinotectal tract - automatic body pain spinovisual reflection
- TRACT STS: spinothalamic system - body pain transfer
- TRACT ASTT: anterior spinothalamic tract (paleospinothalamic anterolateral tract) - body slow pain localization
- TRACT LSTT: lateral spinothalamic tract (neospinothalamic tract) - body pain perception
- TRACT TTS: trigeminothalamic system - head pain transfer
- TRACT ATTT: anterior trigeminothalamic tract (ventral trigeminothalamic tract) - head pain localization
- TRACT DTTT: dorsal trigeminal tract (dorsal trigeminothalamic tract, lemniscus) - head pain perception
- TRACT SLS: spinolimbic system - autonomic body pain transfer
- TRACT MLS: medial lemniscus system - conscious body mechanical perception
- TRACT PCS: posterior column system (dorsal column, Reils band, Reils ribbon) - conscious upper body mechanical and lower body cutaneous perception
- TRACT SCVT: spinocervical tract (Morin's tract) - conscious lower body proprioception
- TRACT SCS: spinocerebellar system - automatic activity
- TRACT DSCS: direct spinocerebellar system - automatic activity of body
- TRACT CSCT: cuneocerebellar tract - automatic activity of upper limbs
- TRACT DSCT: dorsal spinocerebellar tract (posterior spinocerebellar tract, Flechsigs tract) - automatic activity of lower limbs
- TRACT RSCT: rostral spinocerebellar tract - automatic activity of upper body
- TRACT VSCT: ventral spinocerebellar tract (anterior spinocerebellar tract, Gowers tract) - automatic activity of lower body
- TRACT SMTS: spinometencephalic system - automatic activity integration
- TRACT DSCS: direct spinocerebellar system - automatic activity of body
Descending Tracts
TRACT SET: Descending Tracts
- TRACT ATS: autonomic tracts system (descending autonomic fibers) - autonomic control
- TRACT HTST: hypothalamospinal tract - oculomotor autonomic control
- TRACT SSS: solitariospinal system - involuntary breathing control
- TRACT SSET: solitariospinal expiratory tract - rhythmic expiration
- TRACT SSIT: solitariospinal inpiratory tract - rhythmic inspiration
- TRACT ESS: extensor somatic system - extensor control
- TRACT ACST: anterior corticospinal tract (ventral corticospinal tract) - conscious extensor control
- TRACT MLFS: medial longitudinal fasciculus system - automatic control
- TRACT TCST: tectospinal tract - oculomotor automatic control
- TRACT VST: vestibulospinal tract - body automatic control
- TRACT LVST: lateral vestibulospinal tract - maintaining balance via legs extensors
- TRACT MVST: medial vestibulospinal tract - stabilize visual image on retina
- TRACT RTSS: reticulospinal system - automatic and autonomic control
- TRACT MRST: medullary reticulospinal tract (lateral reticulospinal tract) - inhibit extensors
- TRACT PRST: pontine reticulospinal tract (medial reticulospinal tract) - excite extensors
- TRACT FSS: flexor somatic system - flexor control
- TRACT CBT: corticobulbar tract - cranial flexor control
- TRACT LSTT: lateral corticospinal tract - conscious flexor control
- TRACT RBST: rubrospinal tract - automatic flexor control