Difference between revisions of "BrainRegionLPC HT PRF PB"
From aHuman Wiki
(Automated page entry using MWPush.pl) |
(Automated page entry using MWPush.pl) |
||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
* [http://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S0149763401000215-gr4a.gif Gustatory sensory system of rat and macaque] - see [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0149763401000215 Reference] | * [http://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S0149763401000215-gr4a.gif Gustatory sensory system of rat and macaque] - see [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0149763401000215 Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S0149763401000215-gr4a.gif" alt="unavailable"> | + | <img src="http://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S0149763401000215-gr4a.gif" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;"> |
* [http://www.pnas.org/content/103/32/12150/F7.large.jpg Food-entrainable circadian oscillator] - see [http://www.pnas.org/content/103/32/12150/F7.expansion.html Reference] | * [http://www.pnas.org/content/103/32/12150/F7.large.jpg Food-entrainable circadian oscillator] - see [http://www.pnas.org/content/103/32/12150/F7.expansion.html Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://www.pnas.org/content/103/32/12150/F7.large.jpg" alt="unavailable"height=300> | + | <img src="http://www.pnas.org/content/103/32/12150/F7.large.jpg" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;" height=300> |
* [http://www.nature.com/nrendo/journal/v6/n8/images/nrendo.2010.93-f1.jpg Bowels control brain: gut hormones and obesity] - see [http://www.nature.com/nrendo/journal/v6/n8/fig_tab/nrendo.2010.93_F1.html Reference] | * [http://www.nature.com/nrendo/journal/v6/n8/images/nrendo.2010.93-f1.jpg Bowels control brain: gut hormones and obesity] - see [http://www.nature.com/nrendo/journal/v6/n8/fig_tab/nrendo.2010.93_F1.html Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://www.nature.com/nrendo/journal/v6/n8/images/nrendo.2010.93-f1.jpg" alt="unavailable"> | + | <img src="http://www.nature.com/nrendo/journal/v6/n8/images/nrendo.2010.93-f1.jpg" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;"> |
* [http://www.intechopen.com/source/html/40109/media/image1.jpeg Physiology and pathophysiology of lower urinary tract] - see [http://www.intechopen.com/books/computational-intelligence-in-electromyography-analysis-a-perspective-on-current-applications-and-future-challenges/sphincter-emg-for-diagnosing-multiple-system-atrophy-and-related-disorders Reference] | * [http://www.intechopen.com/source/html/40109/media/image1.jpeg Physiology and pathophysiology of lower urinary tract] - see [http://www.intechopen.com/books/computational-intelligence-in-electromyography-analysis-a-perspective-on-current-applications-and-future-challenges/sphincter-emg-for-diagnosing-multiple-system-atrophy-and-related-disorders Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://www.intechopen.com/source/html/40109/media/image1.jpeg" alt="unavailable"> | + | <img src="http://www.intechopen.com/source/html/40109/media/image1.jpeg" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;"> |
* [http://neuropolitics.org/connect-amygdala.jpg Amygdalar disruption of prefrontal cortex] - see [http://neuropolitics.org/defaultmay10.asp Reference] | * [http://neuropolitics.org/connect-amygdala.jpg Amygdalar disruption of prefrontal cortex] - see [http://neuropolitics.org/defaultmay10.asp Reference] | ||
| − | <img src="http://neuropolitics.org/connect-amygdala.jpg" alt="unavailable"> | + | <img src="http://neuropolitics.org/connect-amygdala.jpg" alt="unavailable" style="max-width: 100%;"> |
Revision as of 09:07, 7 September 2015
Parabrachial Nucleus
@@Home -> BiologicalLifeResearch -> BrainAreaLPC -> BrainRegionLPC_HT_PRF_PB
This page covers biological details of component Parabrachial Nucleus. Region is part of aHuman target integrated biological model.
- Top-down path to region: Hindbrain Metencephalon -> Pontine Reticular Formation (HT.RF) -> Pontine Reticular Formation, Lateral Column (HT.RF.LAT) -> Parabrachial Nucleus (LPC.HT.PRF.PB) (see Mind Maps)
- Type: nucleus
- Brain area: Lower Brain - Peripheral Control Area
- Role: relay
- Function: Source of short-latency nociceptive input; sense of physiological condition of body well-being or interoception
- Notes to function: major relay site for visceral afferents ascending through ventrobasal thalamus and terminating in insular cortex
(generated)
Components
(generated)
Component items:
- Subbrachial Nucleus
- Lateral Parabrachial Nucleus
- External Lateral Parabrachial Nucleus
- Medial Parabrachial Nucleus
Connectivity
(generated)
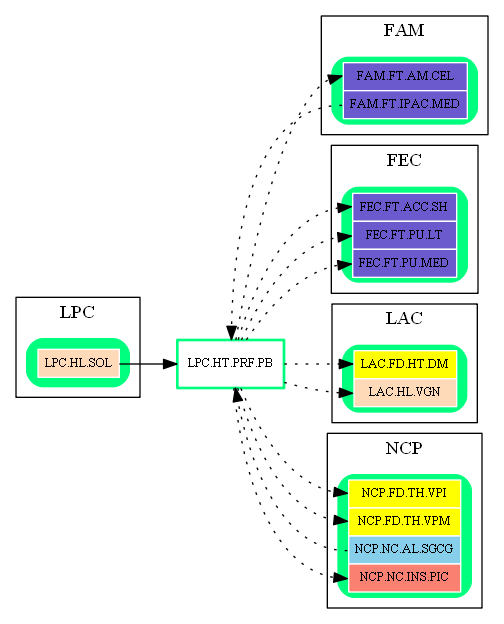
Inbound Region Connections:
| Source Area | Source Region | Source Name | Type | Reference |
| FAM | FAM.FT.IPAC.MED | Medial Interstitial Anterior Commissural Nucleus | excitatory-glu | (unknown reference) |
| LPC | LPC.HL.SOL | Solitary Nucleus | excitatory-glu | Amygdalar disruption of prefrontal cortex (SOL -> PB) |
| NCP | NCP.NC.AL.SGCG | Subgenual Cingulate Cortex | excitatory-glu | Global visual system (FrontalCortex -> RF, abstract) |
Outbound Region Connections:
Thirdparty Circuits
(generated)





References
(generated)
- http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0149763401000215
- http://www.pnas.org/content/103/32/12150/F7.expansion.html
- http://www.nature.com/nrendo/journal/v6/n8/fig_tab/nrendo.2010.93_F1.html
- http://www.intechopen.com/books/computational-intelligence-in-electromyography-analysis-a-perspective-on-current-applications-and-future-challenges/sphincter-emg-for-diagnosing-multiple-system-atrophy-and-related-disorders
- http://neuropolitics.org/defaultmay10.asp