BrainPictures
From aHuman Wiki
Revision as of 01:17, 16 June 2015 by Admin (Talk | contribs) (Automated page entry using MWPush.pl)
Neocortex Research
Home -> BrainPictures
<wiki:toc max_depth="2" />
Contents
Biological Overview
Biological Hierarchy
Links to Common Terms

- head
* sensors * sensor data tract * sensor control tract * brain
- body (spinal cord)
* effectors * body feeling components * body feeling data tract * body feeling modulation tract * effectors control tract * effectors feedback tract * effectors feeling tract
Biological Model
Biological Module View

Modules are defined as follows:
| Module and allocated areas | Functions | Flows |
|---|---|---|
|
* capture events from external world * capture static data from external world * expressing sensing behaviour
* perceptions of various modalities * pay attention to selected area / overt attention * tracking objects / covert attention * saccadic perception / covert attention |
* (External World) -> sensor data * PCA -> BSA -> low-level sensory control in perception * ACA -> BSA -> attention area selection
* sensory data -> BSA * perception control feedback -> THA -> PCA * attention sensor control feedback -> THA -> ACA * sensory state expression -> (External World) |
* thalamus * hypothalamus
* septal nuclei |
* visceral control center of the body * relaying sensation, spatial sense and motor signals to the cerebral cortex * regulation of consciousness, sleep and alertness * control memory, attention and alertness * controller of theta rhythm
* effector control system * perceptions of various modalities * cortical regulation of the thalamic activity * modulatory, life support and the sleep/wake cycle * attention, planning, organization * abstract thinking, multi-tasking and active memory |
* BSA -> sensor data -> PCA * BSA -> sensor data (lateral posterior nucleus, pulvinar) -> HCA * BSA -> perception (intralaminar) -> BGA * BSA -> cerebellum effector control feedback -> ACA * BSA -> body sensations -> ACA * BSA -> pain -> PCA * HCA -> alerts, (anterior/medial nuclei) -> ACA * BGA -> sensory data (ventral posterolateral/posteromedial nucleus) -> ACA * BGA -> striatum effector control feedback -> ACA
* PCA -> (medial nuclei) -> PCA * HCA -> (anterior nuclei) -> HCA * ACA -> (medial nuclei) -> ACA |
* primary somatosensory cortex
* cingulate cortex * anterior cingulate cortex |
* self-consciousness / personality / identity * top-level complex planning / imagination * inhibition control * model of good ideal behaviour / morality * top-level patterned effector actions * cortex individual effector actions and sensor control * top-level error and conflict detection * guide task selection * monitor progress * basic sensations of the body * working memory
* sensory integration * representing the affective value of reinforcers * decision-making |
* BGA -> THA -> sensory data * PCA -> perception data * HCA -> past experience * HCA -> reward signals (orbitomedial PFC) * BSA -> THA -> body senses * THA -> bioregulatory responses
* current converged sensory input (pcf) -> HCA * motor/behavioral commands -> PCA * reward, feedback to bias flow along expectation -> PCA * motor control -> BSA * anti-inhibitory emotional context -> BGA * inhibitory emotional context -> BGA * guidance of movement -> BGA * (premotor) -> THA |
* superior parietal lobule * inferior parietal lobule * intraparietal sulcus * general interpretation area
* cingulate cortex * posterior cingulate cortex |
* body sensations relationships / body image * opinions * simple specific sensor spatial primitives * intermediate specific sensor spatial and temporal patterns * object representation from specific sensor * episodic memory, emotion, navigation, resting
* semantics * reading both in regards to meaning and phonology * guidance of limb and eye movement |
* HSA -> BSA -> THA -> sensory data * HSA -> BSA -> THA -> sensory perception control feedback * HCA -> THA -> long-term memory sequences * BSA -> THA -> pain * ACA -> reward, feedback to bias flow along expectation
* sensory data -> HCA * associations -> THA -> ACA * guide saccadic perception -> BSA -> HSA * feelings -> ACA |
* hippocampus * fornix |
* specific sensor perception and memory * working memory * autobiographical/declarative/episodic memories * formation and storing spatial declarative memory * encoding and recognition of scenes, spatial relations * detection of novel events, places and stimuli, spatial coding * distinguishing multiple instances of similar events, multiple visits to the same location * emotional and affective state * distinguishing stress and depression * assigning stimuli to categorical classes * habits, visceral sensations
* memory consolidation * memory optimization in sleep * recognition and identification of environmental stimuli |
* PCA -> primary and secondary sensory perception * PCA -> polymodal/associative sensory perception * ACA -> converged sensory input * BSA -> sensory input (hierarchical sensory pathway) * THA -> emotional stimulus * THA -> modulatory inputs * THA (septum) -> (fornix) -> initiation of hippocampal thata-rithm
* sensory association -> BGA * reward signals -> ACA * past experience -> ACA * mismatch signal (to raise ACh in HC to facilitate encoding) -> THA (septum) * match signal (to attenuate ACh in HC to facilitate retrieval) -> THA (septum) |
* basal ganglia * amygdala |
* starting, stopping and monitoring movement * inhibit unnecessary movement * planning and modulation of actions, regulate actions * reward, pleasure, addiction, fear * reward and incentive motivation * acquisition and maintenance of a new strategy * mediate learning about irrelevant stimuli * action selection * block slow thinking * quick threat assessment * signalling cortex of motivationally significant stimuli
* learning and memory system * influence various types of learning |
* ACA -> anti-inhibitory emotional context * ACA -> inhibitory emotional context * HCA -> sensory association
* regulation -> ACA * cognition -> ACA * instant actions -> BSA * sensory data (auditory, dorsal auditory pathway) -> PCA |
|
* autonomic behavior, autonomic, involuntary functions * integrate sensors and effectors for precise timing of actions * maintain wakefulness and attention * modulation of outbound effectors information * preliminary specific sensor processing * complex actions, sequential thinking * attention, coordination, precision, and accurate timing * inhibits neuronal maturation
* control of specific sensor * many unconscious homeostatic and reflexive pathways * sensor control, effector planning * reward seeking, learning, and addiction * sleep, equilibrium, sensor control, expressing emotions * control actions power and coordination of multiple actions * control cerebellum/basal ganglia/neocortex effector actions * planning actions |
* TBD
* TBD |
|
* body feeling * affect general body state * generating proprioceptive information * conveys inconscient proprioceptive information
* activate effectors * distal effector actions |
* TBD
* TBD |
Biological Paths
- [pathway connecting the posterior part of the temporoparietal junction with the frontal cortex]
- [pathway transmitting fine touch, vibration and conscious proprioceptive information from the body to the cerebral cortex]
- [pathway originating in the spinal cord and transmitting pain, temperature, itch and crude touch to the thalamus]
- [arising from motor area of the cerebral cortex and controlling movement of ipsilateral limbs]
- [conducting voluntary motor impulses from primary motor cortex to the motor centers of the cord]
- [connecting the cerebral cortex to the medulla in brainstem, controlling muscles of the face, head and neck]
- [connecting the left and right cerebral hemispheres and facilitating interhemispheric communication]
- [connecting ventral tegmentum to frontal cerebral cortex, involved in motivation and emotional response]
- [begins in midbrain and connects to striatum, amygdala, hippocampus, medial prefrontal cortex]
- [connecting substantia nigra with striatum, involved in production of movement]
- [pathway, involved in regulation of lactation, menstrual cycle, vision, blood flow and sexual functions]
- [stream travels to the temporal lobe and is involved with object identification]
- [stream stretches from the primary visual cortex (V1) in the occipital lobe forward into the parietal lobe]
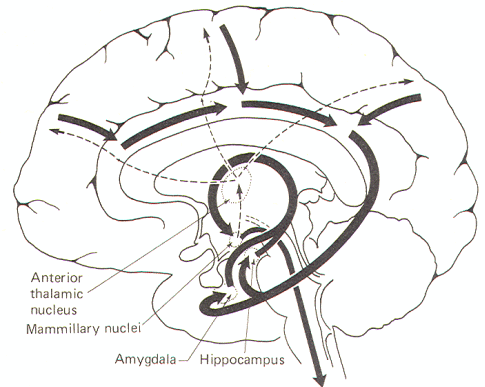
- [circuit, one of major pathways of limbic system and is involved in cortical control of emotion]
Biological Life Pictures
Operating of the mind as a whole. Mind parts.