SpinalCordOld
From aHuman Wiki
Revision as of 19:10, 28 November 2018 by Admin (Talk | contribs) (Automated page entry using MWPush.pl)
Spinal Cord
Home -> BiologicalLifeResearch -> SpinalCord
This page is intended to discover component structure of spinal cord of biological human, sitting in between mind and peripheral organs.
Contents
[hide]SPINAL CORD STRUCTURE
BASIC INFORMATIOIN

- regions - cervical (C1-C8), thoracic (T1-T12), lumbar (L1-L5), sacral (S1-S5), coccygeal (CX = CX1-CX3)
- width - 1 cm (thoracic/sacral) /2 cm (cervical-lumbar)
- height - 45 cm (men)/43 cm (women)
SPINAL CORD SENSORY AND MOTOR ROOTS NEURONS
Fibers by thickness:
- A-alpha motor/sensory (Ia, Ib): 12-22 mcm, 70-120 m/sec, low theshold, 2ms after stimulus (motoneurons, touch, position and velocity, Meissner's corpuscles)
- A-alpha-Ia motor/sensory:
- muscle spindle primary sensory endings (skin, two-point discrimination, extrafusal muscles, Meissner's corpuscles)
- alpha motoneurons (extrafusal muscle fibers, skeletal movements, brainstem/spinal cord)
- FF-type alpha motoneurons - biggest motoneurons, type IIB extrafusal muscle fibers (generate large force, poor efficiency, affected by static beta motoneurons)
- FR alpha motoneurons - type IIA extrafusal muscle fibers (affected by static beta motoneurons)
- S-type alpha motoneurons - type I muscle fibers (little force, metabolically efficient, affected by dynamic beta motoneurons)
- A-alpha-Ib sensory:
- sensory Golgi tendon organs
- sensory Ruffini endings in skin
- A-alpha-Ia motor/sensory:
- A-beta motor/sensory (II): 8-13 mcm, 40-70 m/sec, higher theshold, 4ms after stimulus (fine touch, kinesthesia, muscle spindle secondary endings)
- Merkel disks (weak position and strong velocity - irregular discharge, type I, hairy/hairless skin)
- Ruffini's corpuscles (strong position and weak velocity receptors - regular discharge, type II, hairy/hairless skin)
- Hairy skin velocity receptors (large hair follicles, slow and rapid movement of hairs and deflection of the skin)
- Pacinian corpuscles (transient receptors, connective tissue, vibration, intrafusal muscles, tonic proprioceptive endings, flower-spray type)
- beta motoneurons (skeleto-fusimotor, intrafusal fibers and collaterals to extrafusal muscle fibers, muscle spindles, increase dynamic sensitivity of ending)
- beta dynamic motoneurons - type I extrafusal muscle fibers and the intrafusal bag1 fiber (slow contracting motor units)
- beta static motoneurons - type IIA or IIB extrafusal fibers and the intrafusal bag2 fiber (fast contracting motor units)
- A-gamma motor: 4-8 mcm, 15-40 m/sec, 6ms after stimulus
- intrafusal muscle fibers (skeletal muscle tone, contract muscle spindles from both ends, fusimotor gamma neurons, affect Ia/II)
- gamma static motoneurons - intrafusal bag2 fiber and the nuclear chain fibers
- gamma dynamic motoneurons - intrafusal bag1 fiber
- intrafusal muscle fibers (skeletal muscle tone, contract muscle spindles from both ends, fusimotor gamma neurons, affect Ia/II)
- A-delta sensory (III): 1-4 mcm, 5-15 m/sec, 20ms after stimulus
- noxious receptors (first/fast, sharp, well-localized pain)
- cold receptors (temperature, high-threshold mechano/heat, phasic)
- pressure (rapidly adapting mechanosensitive, directional selectivity, crude touch)
- B motor: 1-3 mcm, 3-14 m/sec, preganglionic autonomic, myelinated, ACh (sympathetic only in T1-L3, IML)
- preganglionic paravertebral sympathetic (short to paravertebral sympathetic ganglia, close to vertebral, fibers ascend/descend to reach all spinal cord levels)
- preganglionic prevertebral sympathetic (long to prevertebral sympathetic ganglia, celiac, superior/inferior mesenteric ganglia)
- preganglionic parasympathetic spinal (spinal cord long fibers to parasympathetic ganglia, splantic nerves, abdominal organs)
- preganglionic parasympathetic cranial (cranial nerves III, VII, IX and X long fibers to parasympathetic ganglia, eye iris, lacrimal/submandibular/subingual glands, thorax, abdomen, GI tract)
- C motor/sensory (IV): 0.1-1 mcm, 0.2-2 m/sec, 60ms after stimulus (pain, touch, pressure, temperature, postganglionic autonomic)
- C fiber nociceptors (responsible for the second, burning pain)
- C fiber warming specific receptors (responsible for warmth)
- ultra-slow histamine-selective C fibers (responsible for itch)
- tactile C fibers (sensual touch, includes CT fibres, also known as C low-threshold mechanoreceptors (CLTM), which are unmyelinated afferents found in human hairy skin, and have a low mechanical threshold < 5 milliNewtons. They have moderate adaptation and may exhibit fatigue on repetitive stimulation and "afterdischarges" for several seconds after a stimulus)
- C mechano- and metabo- receptors in muscles or joints (responsible for muscle exercise, burn and cramp)
- postganglionic sympathetic C fibers (muscles and skin, pre/post - temporal summation and spatial summation, one-to-many, wide-spread, long and unmyelinated, NE)
- postganglionic parasympathetic C fibers (from ganglia in/on wall of organ, visceral activity and repose, short, local)
Sensory neurons:

- Classification by receptor:
- proprioceptors: LI,LV, also LII (fast pain/temperature senses), A-delta fibers
- nociceptors: LII,LI (slow pain/temperature senses, unmyelinated), C fibers
- mechanoreceptors: LIII,LIV (touch/position/kinesthetic/vibration senses), A-alpha-Ia/A-beta fibers

- Proprioception
- receptors origin: muscle spindle (intrafusal fibers), Golgi tendon organ, A-alpha-Ib/A-beta fibers
- intrafusal fiber types:
- nuclear chain fibers - report static length of muscle (aligned in a single row), A-alpha-Ia/A-beta/A-gamma fibers
- static nuclear bag fibers - report static length of muscle (bundle in fiber middle), A-alpha-Ia/A-beta/A-gamma fibers
- dynamic nuclear bag fibers - report rate of change of muscle length (bundle in fiber middle), A-alpha-Ia/A-gamma fibers
- roman number fiber classification:
- Ia - primary afferents, annulospiral endings, length and velocity, A-alpha-Ia fibers
- Ib - Golgi tendon organ, report load being applied to muscle, A-alpha-Ib fibers
- II - secondary afferents, flower spray endings, length only, A-beta fibers
- Sensory endings
-

- Hair follicle receptors: touch (slowly adapting, low threshold), A-beta fibers
- Merkel disk receptors: vibration 5-15 Hz (high resolution tactile discrimination, static touch/pressure, mechanoceptors in hairless skin and mucosa, pressure and texture, slowly adapting, sustained response, low threshold), A-beta fibers
- Meissner's corpuscles: vibration 20-50 Hz (tactile, dynamic touch/pressure, texture, rapidly adapting, superficial papillary receptor, low threshold, especially sensitive to light touch - like fingers and lips), A-alpha-Ia fibers
- Pacinian corpuscles: vibration 60-400 Hz (deep receptors, subcutaneous tissue, viscera, rapidly adaptng, low threshold), A-beta fibers
- Ruffini's corpuscles: stretching of skin (deep receptors, slowly adapting, low threshold), A-alpha-Ib/A-beta fibers
- Free nerve endings: pain, temperature, crude touch, A-delta/C fibers
- Golgi tendon organs: muscle tension (slowly adapting, low threshold), A-alpha-Ib fibers
- Muscle spindles: skeletal muscle, stretch by muscle length (fast), A-alpha-Ia/A-beta
-
Motoneurons:

- alpha-motoneuron: extrafusal muscle fibres (voluntary movement), A-alpha-1a fibers
- beta-motoneuron: intrafusal/extrafusal muscle fibres (voluntary movement), A-beta fibers
- gamma-motoneuron: intrafusal muscle fibers (muscle tonus, additional contracts to maintain sensitivity in stretched state), A-gamma fibers
- preganglionic autonomic: B fibers
- postganglionic autonomic: C fibers
- renshaw cell: axon collateral of alpha-motoneuron -> renshaw cell -> alpha-motoneuron (negative feedback)
Motor interneurons:

- interneurons of indirect supraspinal connections: primary pathway for alpha-motoneurons
- renshaw interneurons: interneurons of direct monosynaptic connections with alpha-motoneurons, some fibers of CST/LVST/RST, negative feedback on the same alpha-neurons; stop firing to be ready for next supraspinal signal
- integrated rhythmic movements of upper and lower extremities like walking and running
- intersegmental interneurons: reciprocal inhibition (excite agonist muscles/ inhibit antagonist muscles), feedback inhibition (selectively inhibit LMN to proper pattern in agonist muscle group)
- commissural interneurons: to contralateral neurons (crossed extensor reflexes, alternate rhythms of both upper and lower extremities during running and walking)
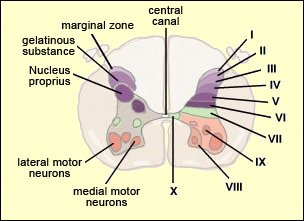
SPINAL CORD NUCLEI

outer:
- Lateral Cervical Nucleus (LCN) (lateral horn, low-threshold fast-conducting, tactile/pressure relay); sensory, tract of Lissauer/spinocervical tract; A-alpha-Ib/A-beta/A-delta sensory data
- Lateral Spinal Nucleus (LSN) (lateral horn, relay in unmyelinated pathways between the periphery and brain, intersegmental integrator); sensory, spinohypothalamic tract/spinosolitary tract; A-delta/C sensory data
sensory:

- Marginal Nucleus (MN), Apex of Posterior Horn, Nucleus Posteromarginalis - LI (A-delta/C, somatic sensory, non-modulatable pain and temperature sensations, joint nociception); sensory, tract of Lissauer/spinomesencephalic tract; modulatory, dorsolateral tract (from RVM); interneurons from SG; interneurons to NPR,IML; A-delta/C sensory data
- Substantia Gelatinosa (SG), Rolando's Substance - LII (C, somatic sensory, short - pain, temperature, long - mechanoreceptors; long inhibits short); sensory, tract of Lissauer; modulatory, dorsolateral fasciculus (from VTA); interneurons to MN, CLN; C sensory data
- Nucleus Proprius (NPR), Main Sensory Nucleus, Proper Sensory Nucleus - LIII,LIV (A-beta, visceral sensory, crude and pressure, 2-point discrimination, vibration); sensory: lateral spinothalamic tract/spinocervical tract/spinotectal tract/spinoolivary tract; A-alpha-Ib/A-beta/A-delta sensory data
- Clarke's Nucleus (CLN), Nucleus Dorsalis, Posterior Thoracic Nucleus, Clarke's Column - LV, LVI (A-alpha/A-delta, visceral sensory, secondary visceral afferents, unconscious proprioception): sensory, tract of Lissauer/anterior spinothalamic tract/spinoreticular tract/dorsal spinocerebellar tract; interneurons from SG, NPR; A-alpha-Ia/A-alpha-Ib/A-delta sensory data
- Central Nucleus (unconscious proprioception)
- Central Cervical Nucleus (CCN) - LVII (spinocerebellar sensory, relays neck proprioception to cerebellum, locomotion); sensory, spinoolivary tract/spinovestibular tract; A-alpha-Ia/A-alpha-Ib sensory data
- Centrobasalis Nucleus (CBN) - LVII (spinocerebellar sensory, relays forelimb proprioception to cerebellum); sensory, rostral spinocerebellar tract; A-alpha-Ia sensory data
- Intermediomedial Nucleus (IMM) - LVII (visceral sensory); sensory, ventral spinocerebellar tract; A-alpha-Ia sensory data
motor:
- Medial Motor Nuclei (axial muscles motor neurons)
- Posteromedial Nucleus (PMN), Dorsomedial Nucleus - LIX (axial trunk flexors, T1-L2); flexor motor, lateral vestibulospinal tract/medullary reticulospinal tract; A-alpha-Ia/A-beta/A-gamma motor data
- Ventromedial Nucleus (VMN), Anteromedial Nucleus - LVIII (axial trunk extensors, inhibit flexors, all segments); extensor motor, ventral corticospinal tract; A-alpha-Ia/A-beta/A-gamma motor data
- Lateral Motor Nuclei (distal muscles motor neurons)
- Posterolateral Nucleus (PLN), Dorsolateral Nucleus - LIX (distal flexors, C4-C8/L2-S1, hand/leg, distal muscles of forearm, hand, leg, foot); flexor/extensor motor, lateral corticospinal tract/rubrospinal tract/lateral vestibulospinal tract; A-alpha-Ia/A-gamma motor data
- Ventrolateral Nucleus (VLN), Anterolateral Nucleus - LIX (distal extensors, C4-C8/L2-S1, shoulder/hip, distal muscles of shoulder girdle, arm, hip, thigh); extensor motor, pontine reticulospinal tract; A-alpha-Ia/A-gamma motor data
- Spinal Accessory Nucleus (SAN) - LIX (neck, control neck to rotate head); flexor motor, tectospinal tract/medial vestibulospinal tract; A-alpha-Ia/A-beta/A-gamma motor data
- Phrenic Nucleus (PHN) - LIX (diaphragm, conscious and autonomic control of breathing); visceral motor, ventral corticospinal tract; autonomic motor, solitariospinal tract; A-alpha-Ia/A-beta/A-gamma motor data
- Retroposterolateral Nucleus (RPL), Retrodorsolateral Nucleus - LIX (fingers, C8-T1/S1-S3, distal large motor neurons to small arm and leg finger muscles); flexor motor, lateral corticospinal tract/rubrospinal tract; A-alpha-Ia/A-gamma motor data
- Onuf's Nucleus (ONN), Gert's Nucleus, Lumbosacral Nucleus - LIX (dorsomedial: urination, dorsolateral: defecation, external sphincters; orgasmic muscular contractions); flexor motor, dorsolateral tract; interneurons from Sacral Parasympathetic Nucleus; A-alpha-Ia/A-gamma motor data
- Dorsal Commissural Nucleus (DCN) - LX (integrate direct/indirect excitatory and inhibitory fast inputs, modulate by slow excitatory responses); interneurons from Intermediolateral Nucleus
autonomic:
- Intermediolateral Cell Column, Intermediate Zone:
- Intermediolateral Nucleus (IML) - LVII (autonomic, visceral structures); sympathetic, visceral motor; dorsolateral tract; interneurons from Marginal Nucleus; B motor data
- Ciliospinal Center (CSC) - LVII (autonomic, visceral structures); sympathetic motor, tectospinal tract/hypothalamospinal tract; B motor data
- Sacral Parasympathetic Nucleus (SPS) - LVII (S1-S3, psym. to large intestine; pelvic nerve); sympathetic motor, dorsolateral tract; interneurons to Onuf's Nucleus; B motor data
SPINAL CORD LAMINAE AND LEVELS
(generated)
 Cuneate Nucleus -> VPL - upper body
Cuneate Nucleus -> VPL - upper body
- DRG -> Gracile Nucleus -> VPL - lower body
- DRG -> Principal Trigeminal Nucleus -> VPM - head and face
SENSORY NUCLEI FROM SPINAL CORD TO VPL/VPM
- DRG -> Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus -> VPM - head and face deep pain/temperature
- DRG -> Marginal Nucleus -> VPL - fast pain/temperature
- DRG -> Substantia Gelatinosa -> VPL - slow pain/temperature
SENSORY NUCLEI FROM SPINAL CORD TO CR
- DRG.CX -> Accessory Cuneate Nucleus -> CR - upper extremity (to C7)
- DRG.TX,LX -> Clarke's Nucleus -> CR - from C8
INTERSPINAL SENSORY TO MOTOR
- vessel/gland (GVA) -> DRG -> Substantia Gelatinosa -> Intermediolateral Nucleus -> (GVE) vessel/gland
- muscle (GSA) -> DRG -> Posteromedial Nucleus/Ventromedial Nucleus/Posterolateral Nucleus/Ventrolateral Nucleus -> (GSE) muscle
- muscle (GSA) -> DRG -> Substantia Gelatinosa -> Posteromedial Nucleus/Ventromedial Nucleus/Posterolateral Nucleus/Ventrolateral Nucleus -> (GSE) muscle