SpinalCordOld
From aHuman Wiki
Revision as of 12:54, 15 June 2016 by Admin (Talk | contribs) (Automated page entry using MWPush.pl)
Spinal Cord
Home -> BiologicalLifeResearch -> SpinalCord
This page is intended to discover component structure of spinal cord of biological human, sitting in between mind and peripheral organs.
SPINAL CORD STRUCTURE
BASIC INFORMATIOIN

- regions - cervical (C1-C8), thoracic (T1-T12), lumbar (L1-L5), sacral (S1-S5), coccygeal (CX = CX1-CX3)
- width - 1 cm (thoracic/sacral) /2 cm (cervical-lumbar)
- height - 45 cm (men)/43 cm (women)
SPINAL CORD SENSORY AND MOTOR ROOTS NEURONS
Fibers by thickness:
- A-alpha motor/sensory (Ia, Ib): 12-22 mcm, 70-120 m/sec, low theshold, 2ms after stimulus (motoneurons, touch, position and velocity, Meissner's corpuscles)
- A-alpha-Ia motor/sensory:
- muscle spindle primary sensory endings (skin, two-point discrimination, extrafusal muscles, Meissner's corpuscles)
- alpha motoneurons (extrafusal muscle fibers, skeletal movements, brainstem/spinal cord)
- FF-type alpha motoneurons - biggest motoneurons, type IIB extrafusal muscle fibers (generate large force, poor efficiency, affected by static beta motoneurons)
- FR alpha motoneurons - type IIA extrafusal muscle fibers (affected by static beta motoneurons)
- S-type alpha motoneurons - type I muscle fibers (little force, metabolically efficient, affected by dynamic beta motoneurons)
- A-alpha-Ib sensory:
- sensory Golgi tendon organs
- sensory Ruffini endings in skin
- A-alpha-Ia motor/sensory:
- A-beta motor/sensory (II): 8-13 mcm, 40-70 m/sec, higher theshold, 4ms after stimulus (fine touch, kinesthesia, muscle spindle secondary endings)
- Merkel disks (weak position and strong velocity - irregular discharge, type I, hairy/hairless skin)
- Ruffini's corpuscles (strong position and weak velocity receptors - regular discharge, type II, hairy/hairless skin)
- Hairy skin velocity receptors (large hair follicles, slow and rapid movement of hairs and deflection of the skin)
- Pacinian corpuscles (transient receptors, connective tissue, vibration, intrafusal muscles, tonic proprioceptive endings, flower-spray type)
- beta motoneurons (skeleto-fusimotor, intrafusal fibers and collaterals to extrafusal muscle fibers, muscle spindles, increase dynamic sensitivity of ending)
- beta dynamic motoneurons - type I extrafusal muscle fibers and the intrafusal bag1 fiber (slow contracting motor units)
- beta static motoneurons - type IIA or IIB extrafusal fibers and the intrafusal bag2 fiber (fast contracting motor units)
- A-gamma motor: 4-8 mcm, 15-40 m/sec, 6ms after stimulus
- intrafusal muscle fibers (skeletal muscle tone, contract muscle spindles from both ends, fusimotor gamma neurons, affect Ia/II)
- gamma static motoneurons - intrafusal bag2 fiber and the nuclear chain fibers
- gamma dynamic motoneurons - intrafusal bag1 fiber
- intrafusal muscle fibers (skeletal muscle tone, contract muscle spindles from both ends, fusimotor gamma neurons, affect Ia/II)
- A-delta sensory (III): 1-4 mcm, 5-15 m/sec, 20ms after stimulus
- noxious receptors (first/fast, sharp, well-localized pain)
- cold receptors (temperature, high-threshold mechano/heat, phasic)
- pressure (rapidly adapting mechanosensitive, directional selectivity, crude touch)
- B motor: 1-3 mcm, 3-14 m/sec, preganglionic autonomic, myelinated, ACh (sympathetic only in T1-L3, IML)
- preganglionic paravertebral sympathetic (short to paravertebral sympathetic ganglia, close to vertebral, fibers ascend/descend to reach all spinal cord levels)
- preganglionic prevertebral sympathetic (long to prevertebral sympathetic ganglia, celiac, superior/inferior mesenteric ganglia)
- preganglionic parasympathetic spinal (spinal cord long fibers to parasympathetic ganglia, splantic nerves, abdominal organs)
- preganglionic parasympathetic cranial (cranial nerves III, VII, IX and X long fibers to parasympathetic ganglia, eye iris, lacrimal/submandibular/subingual glands, thorax, abdomen, GI tract)
- C motor/sensory (IV): 0.1-1 mcm, 0.2-2 m/sec, 60ms after stimulus (pain, touch, pressure, temperature, postganglionic autonomic)
- C fiber nociceptors (responsible for the second, burning pain)
- C fiber warming specific receptors (responsible for warmth)
- ultra-slow histamine-selective C fibers (responsible for itch)
- tactile C fibers (sensual touch, includes CT fibres, also known as C low-threshold mechanoreceptors (CLTM), which are unmyelinated afferents found in human hairy skin, and have a low mechanical threshold < 5 milliNewtons. They have moderate adaptation and may exhibit fatigue on repetitive stimulation and "afterdischarges" for several seconds after a stimulus)
- C mechano- and metabo- receptors in muscles or joints (responsible for muscle exercise, burn and cramp)
- postganglionic sympathetic C fibers (muscles and skin, pre/post - temporal summation and spatial summation, one-to-many, wide-spread, long and unmyelinated, NE)
- postganglionic parasympathetic C fibers (from ganglia in/on wall of organ, visceral activity and repose, short, local)
Sensory neurons:

- Classification by receptor:
- proprioceptors: LI,LV, also LII (fast pain/temperature senses), A-delta fibers
- nociceptors: LII,LI (slow pain/temperature senses, unmyelinated), C fibers
- mechanoreceptors: LIII,LIV (touch/position/kinesthetic/vibration senses), A-alpha-Ia/A-beta fibers

- Proprioception
- receptors origin: muscle spindle (intrafusal fibers), Golgi tendon organ, A-alpha-Ib/A-beta fibers
- intrafusal fiber types:
- nuclear chain fibers - report static length of muscle (aligned in a single row), A-alpha-Ia/A-beta/A-gamma fibers
- static nuclear bag fibers - report static length of muscle (bundle in fiber middle), A-alpha-Ia/A-beta/A-gamma fibers
- dynamic nuclear bag fibers - report rate of change of muscle length (bundle in fiber middle), A-alpha-Ia/A-gamma fibers
- roman number fiber classification:
- Ia - primary afferents, annulospiral endings, length and velocity, A-alpha-Ia fibers
- Ib - Golgi tendon organ, report load being applied to muscle, A-alpha-Ib fibers
- II - secondary afferents, flower spray endings, length only, A-beta fibers
- Sensory endings
-

- Hair follicle receptors: touch (slowly adapting, low threshold), A-beta fibers
- Merkel disk receptors: vibration 5-15 Hz (high resolution tactile discrimination, static touch/pressure, mechanoceptors in hairless skin and mucosa, pressure and texture, slowly adapting, sustained response, low threshold), A-beta fibers
- Meissner's corpuscles: vibration 20-50 Hz (tactile, dynamic touch/pressure, texture, rapidly adapting, superficial papillary receptor, low threshold, especially sensitive to light touch - like fingers and lips), A-alpha-Ia fibers
- Pacinian corpuscles: vibration 60-400 Hz (deep receptors, subcutaneous tissue, viscera, rapidly adaptng, low threshold), A-beta fibers
- Ruffini's corpuscles: stretching of skin (deep receptors, slowly adapting, low threshold), A-alpha-Ib/A-beta fibers
- Free nerve endings: pain, temperature, crude touch, A-delta/C fibers
- Golgi tendon organs: muscle tension (slowly adapting, low threshold), A-alpha-Ib fibers
- Muscle spindles: skeletal muscle, stretch by muscle length (fast), A-alpha-Ia/A-beta
-
Motoneurons:

- alpha-motoneuron: extrafusal muscle fibres (voluntary movement), A-alpha-1a fibers
- beta-motoneuron: intrafusal/extrafusal muscle fibres (voluntary movement), A-beta fibers
- gamma-motoneuron: intrafusal muscle fibers (muscle tonus, additional contracts to maintain sensitivity in stretched state), A-gamma fibers
- preganglionic autonomic: B fibers
- postganglionic autonomic: C fibers
- renshaw cell: axon collateral of alpha-motoneuron -> renshaw cell -> alpha-motoneuron (negative feedback)
Motor interneurons:

- interneurons of indirect supraspinal connections: primary pathway for alpha-motoneurons
- renshaw interneurons: interneurons of direct monosynaptic connections with alpha-motoneurons, some fibers of CST/LVST/RST, negative feedback on the same alpha-neurons; stop firing to be ready for next supraspinal signal
- integrated rhythmic movements of upper and lower extremities like walking and running
- intersegmental interneurons: reciprocal inhibition (excite agonist muscles/ inhibit antagonist muscles), feedback inhibition (selectively inhibit LMN to proper pattern in agonist muscle group)
- commissural interneurons: to contralateral neurons (crossed extensor reflexes, alternate rhythms of both upper and lower extremities during running and walking)
SPINAL CORD NUCLEI

outer:
- Lateral Cervical Nucleus (LCN) (lateral horn, low-threshold fast-conducting, tactile/pressure relay); sensory, tract of Lissauer/spinocervical tract; A-alpha-Ib/A-beta/A-delta sensory data
- Lateral Spinal Nucleus (LSN) (lateral horn, relay in unmyelinated pathways between the periphery and brain, intersegmental integrator); sensory, spinohypothalamic tract/spinosolitary tract; A-delta/C sensory data
sensory:

- Marginal Nucleus (MN), Apex of Posterior Horn, Nucleus Posteromarginalis - LI (A-delta/C, somatic sensory, non-modulatable pain and temperature sensations, joint nociception); sensory, tract of Lissauer/spinomesencephalic tract; modulatory, dorsolateral tract (from RVM); interneurons from SG; interneurons to NPR,IML; A-delta/C sensory data
- Substantia Gelatinosa (SG), Rolando's Substance - LII (C, somatic sensory, short - pain, temperature, long - mechanoreceptors; long inhibits short); sensory, tract of Lissauer; modulatory, dorsolateral fasciculus (from VTA); interneurons to MN, CLN; C sensory data
- Nucleus Proprius (NPR), Main Sensory Nucleus, Proper Sensory Nucleus - LIII,LIV (A-beta, visceral sensory, crude and pressure, 2-point discrimination, vibration); sensory: lateral spinothalamic tract/spinocervical tract/spinotectal tract/spinoolivary tract; A-alpha-Ib/A-beta/A-delta sensory data
- Clarke's Nucleus (CLN), Nucleus Dorsalis, Posterior Thoracic Nucleus, Clarke's Column - LV, LVI (A-alpha/A-delta, visceral sensory, secondary visceral afferents, unconscious proprioception): sensory, tract of Lissauer/anterior spinothalamic tract/spinoreticular tract/dorsal spinocerebellar tract; interneurons from SG, NPR; A-alpha-Ia/A-alpha-Ib/A-delta sensory data
- Central Nucleus (unconscious proprioception)
- Central Cervical Nucleus (CCN) - LVII (spinocerebellar sensory, relays neck proprioception to cerebellum, locomotion); sensory, spinoolivary tract/spinovestibular tract; A-alpha-Ia/A-alpha-Ib sensory data
- Centrobasalis Nucleus (CBN) - LVII (spinocerebellar sensory, relays forelimb proprioception to cerebellum); sensory, rostral spinocerebellar tract; A-alpha-Ia sensory data
- Intermediomedial Nucleus (IMM) - LVII (visceral sensory); sensory, ventral spinocerebellar tract; A-alpha-Ia sensory data
motor:
- Medial Motor Nuclei (axial muscles motor neurons)
- Posteromedial Nucleus (PMN), Dorsomedial Nucleus - LIX (axial trunk flexors, T1-L2); flexor motor, lateral vestibulospinal tract/medullary reticulospinal tract; A-alpha-Ia/A-beta/A-gamma motor data
- Ventromedial Nucleus (VMN), Anteromedial Nucleus - LVIII (axial trunk extensors, inhibit flexors, all segments); extensor motor, ventral corticospinal tract; A-alpha-Ia/A-beta/A-gamma motor data
- Lateral Motor Nuclei (distal muscles motor neurons)
- Posterolateral Nucleus (PLN), Dorsolateral Nucleus - LIX (distal flexors, C4-C8/L2-S1, hand/leg, distal muscles of forearm, hand, leg, foot); flexor/extensor motor, lateral corticospinal tract/rubrospinal tract/lateral vestibulospinal tract; A-alpha-Ia/A-gamma motor data
- Ventrolateral Nucleus (VLN), Anterolateral Nucleus - LIX (distal extensors, C4-C8/L2-S1, shoulder/hip, distal muscles of shoulder girdle, arm, hip, thigh); extensor motor, pontine reticulospinal tract; A-alpha-Ia/A-gamma motor data
- Spinal Accessory Nucleus (SAN) - LIX (neck, control neck to rotate head); flexor motor, tectospinal tract/medial vestibulospinal tract; A-alpha-Ia/A-beta/A-gamma motor data
- Phrenic Nucleus (PHN) - LIX (diaphragm, conscious and autonomic control of breathing); visceral motor, ventral corticospinal tract; autonomic motor, solitariospinal tract; A-alpha-Ia/A-beta/A-gamma motor data
- Retroposterolateral Nucleus (RPL), Retrodorsolateral Nucleus - LIX (fingers, C8-T1/S1-S3, distal large motor neurons to small arm and leg finger muscles); flexor motor, lateral corticospinal tract/rubrospinal tract; A-alpha-Ia/A-gamma motor data
- Onuf's Nucleus (ONN), Gert's Nucleus, Lumbosacral Nucleus - LIX (dorsomedial: urination, dorsolateral: defecation, external sphincters; orgasmic muscular contractions); flexor motor, dorsolateral tract; interneurons from Sacral Parasympathetic Nucleus; A-alpha-Ia/A-gamma motor data
- Dorsal Commissural Nucleus (DCN) - LX (integrate direct/indirect excitatory and inhibitory fast inputs, modulate by slow excitatory responses); interneurons from Intermediolateral Nucleus
autonomic:
- Intermediolateral Cell Column, Intermediate Zone:
- Intermediolateral Nucleus (IML) - LVII (autonomic, visceral structures); sympathetic, visceral motor; dorsolateral tract; interneurons from Marginal Nucleus; B motor data
- Ciliospinal Center (CSC) - LVII (autonomic, visceral structures); sympathetic motor, tectospinal tract/hypothalamospinal tract; B motor data
- Sacral Parasympathetic Nucleus (SPS) - LVII (S1-S3, psym. to large intestine; pelvic nerve); sympathetic motor, dorsolateral tract; interneurons to Onuf's Nucleus; B motor data
SPINAL CORD LAMINAE AND LEVELS
(generated)
<img src="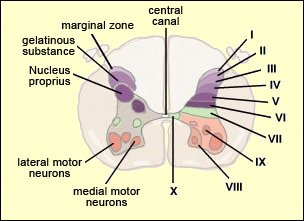 " alt=
" alt=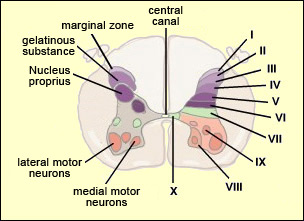
| Level/Lamina | LO | LI | LII | LIII | LIV | LV | LVI | LVII | LVIII | LIX | LX |
| C1 | LCN | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CCN | VMN | SAN | |||
| C2 | LCN | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CCN | VMN | SAN | |||
| C3 | LCN | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CCN | VMN | SAN,PHN | |||
| C4 | LCN | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CCN | VMN | SAN,PHN,PLN,VLN | |||
| C5 | LCN | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CBN | VMN | SAN,PHN,PLN,VLN | |||
| C6 | LCN | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CBN | VMN | SAN,PLN,VLN | |||
| C7 | LCN | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CBN | VMN | PLN,VLN | |||
| C8 | LCN | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CLN | CLN | CBN,RPL | VMN | PLN,VLN | |
| T1 | LSN | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CLN | CLN | IML,IMM,RPL,CSC | VMN | PMN | |
| T2 | LSN | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CLN | CLN | IML,IMM,CSC | VMN | PMN | |
| T3 | LSN | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CLN | CLN | IML,IMM | VMN | PMN | |
| T4 | LSN | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CLN | CLN | IML,IMM | VMN | PMN | |
| T5 | LSN | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CLN | CLN | IML,IMM | VMN | PMN | |
| T6 | LSN | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CLN | CLN | IML,IMM | VMN | PMN | |
| T7 | LSN | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CLN | CLN | IML,IMM | VMN | PMN | |
| T8 | LSN | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CLN | CLN | IML,IMM | VMN | PMN | |
| T9 | LSN | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CLN | CLN | IML,IMM | VMN | PMN | |
| T10 | LSN | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CLN | CLN | IML,IMM | VMN | PMN | |
| T11 | LSN | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CLN | CLN | IML,IMM | VMN | PMN | |
| T12 | LSN | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CLN | CLN | IML,IMM | VMN | PMN | |
| L1 | LSN | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CLN | CLN | IML,IMM | VMN | PMN | DCN |
| L2 | LSN | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CLN | CLN | IML,IMM | VMN | PMN,PLN,VLN | DCN |
| L3 | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | CLN | CLN | VMN | PLN,VLN | |||
| L4 | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | VMN | PLN,VLN | |||||
| L5 | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | VMN | PLN,VLN | |||||
| S1 | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | RPL,SPS | VMN | PLN,VLN,ONN | DCN | |||
| S2 | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | RPL,SPS | VMN | ONN | DCN | |||
| S3 | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | RPL,SPS | VMN | ONN | DCN | |||
| S4 | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | VMN | DCN | |||||
| S5 | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | VMN | ||||||
| CX | MN | SG | NPR | NPR | VMN |
SUBCORTICAL SENSORY SYSTEMS
- subcortical visual system
- somatosensory system
- subcortical auditory system
- gustatory system
- viscerosensory system
- humerosensory system
SPINAL CORD CONNECTIVITY
SPINAL CORD TRACTS


ASCENDING:
- dorsal column, posterior column, medial lemniscus (well-localized discriminative fine touch and proprioception, alpha/beta mechanoreceptors, conscious):
- fasciculus gracilis, tract of Goll (A-beta, tactile and pressure, thoracic-toward-contralateral and cervical slices): receptors of thoracic and lower limbs to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to Gracile Nucleus (N2) to Ventral Posterolateral Nucleus (N3) to Somatosensory Cortex (BA 3b)
- fasciculus cuneatus, tract of Burdach (A-beta, fine touch, fine pressure, vibration, and proprioception, sacral-toward-contralateral and lumbar slices): receptors of C1-T6 dermatomes to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to Cuneate Nucleus (N2) to
- Ventral Posterolateral Nucleus (neck, trunk, and extremities) (N3) to Somatosensory Cortex (BA 3b)
- Ventral Posteromedial Nucleus (head) (N3) to Somatosensory Cortex (BA 3b)
- dorsolateral column, dorsolateral fasciculus, dorsolateral funiculus:
- tract of Lissauer, fasciculus of Lissauer, tract/zone of Lissauer (DLF, intraspinal, discriminative pain and temperature information - location, intensity and quality)
- A-delta (fast, pain duration equals to stimulus duration) pain fibers to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to Marginal Nucleus (N2) to Lateral Cervical Nucleus (N3) (initial sharp localization of pain) to:
- Gracile Nucleus (from medial LSN) (N3) to fasciculus gracilis
- Cuneate Nucleus (from lateral LSN) (N3) to fasciculus cuneatus
- C (slow, pain duration exceeds simulus duration, substance P) pain fibers to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to Substantia Gelatinosa (N2) to Clarke's Nucleus to anterior spinothalamic tract
- A-delta (fast, pain duration equals to stimulus duration) pain fibers to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to Marginal Nucleus (N2) to Lateral Cervical Nucleus (N3) (initial sharp localization of pain) to:
- spinocervical tract, Morin's tract: A-alpha,A-beta receptors (static position, Ruffini endings) to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to Nucleus Proprius (N2) to Lateral Cervical Nucleus (N3) to
- Periaqueductal Gray Matter
- Ventral Posterolateral Nucleus (N4) to neocortex
- tract of Lissauer, fasciculus of Lissauer, tract/zone of Lissauer (DLF, intraspinal, discriminative pain and temperature information - location, intensity and quality)
- lateral sensory tracts:
- anterolateral system:
- spinothalamic tract (STT, conscious):
- trigeminothalamic tract, neospinothalamic tract (TTT):
- head, face and intraoral structures nociceptors to Trigeminal Ganglion (N1) to Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus (N2) to Ventral Posteromedial Nucleus (N3) to Somatosensory Cortex (BA 1,2)
- nociceptors of cranial nerves 7,9,10 to Trigeminal Ganglion, Jugular Ganglion, Nodose Ganglion (N1) to spinal trigeminal nucleus (N2) to Ventral Posteromedial Nucleus (N3) to Somatosensory Cortex (BA 1,2)
- C-fibers of face dull, burning pain, deep, aching pain, temperature and crude touch to Principal Trigeminal Nucleus (N1) to Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus (N2) to Centromedian Nucleus of Thalamus and Parafascicular Nucleus of Thalamus (N3) to Somatosensory Cortex (BA 3)
- paleospinothalamic tract (cervical-anterior-toward-contralateral, thoracic, lumbar, sacral-lateral slices):
- anterior spinothalamic tract, anterolateral tract (ASTT, both sides, non-discriminative touch & pressure): tract of Lissauer to Substantia Gelatinosa to Clarke's Nucleus (N1) to Ventral Posterolateral Nucleus (N2) to Somatosensory Cortex
- lateral spinothalamic tract (LSTT, pain & thermal sense-temperature): free nerve endings (pain and temperature, A-delta/C fibers) to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to
- trigeminothalamic tract, neospinothalamic tract (TTT):
- spinolimbic pathways
- spinohypothalamic tract: A-delta,C fibers to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to Lateral Spinal Nucleus (N2) to hypothalamus (endocrine, motivational responses to stimuli):
- spinomesencephalic tract: A-delta/C fibers to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to Marginal Nucleus (N2) to Periaqueductal Gray Matter
- spinoreticular tract: free nerve endings (crude touch, temperature, pain, afferent for RF, conscious) to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to Clarke's Nucleus (N2) to:
- Medullary Reticular Formation
- Pontine Reticular Formation (Gigantocellular Reticular Nucleus, Oral Pontine Reticular Nucleus, Caudal Pontine Reticular Nucleus) (N3) to Centromedian Nucleus of Thalamus (N4)
- Cuneiform Nucleus (N3) to Centromedian Nucleus of Thalamus (N4)
- spinosolitary tract: C fibers to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to Lateral Spinal Nucleus (N3) to Solitary Nucleus
- spinotectal tract: free nerve endings (ST, crude touch, temperature, pain, spinovisual reflexes, head/eye movement toward stimulus source) to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to Nucleus Proprius (N2) to Deep Superior Colliculus (N3)
- spinometencephalic pathways
- spinoolivary tract, Helweg's tract (SOT, lateral, proprioceptive and cutaneous organs to cerebellum): proprioception information, cutaneous impulses from muscles and tendons to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to Nucleus Proprius, Central Cervical Nucleus (N2) to Inferior Olivary Nucleus (N3) to Cerebellum (automatic movements of head, neck & upper limb)
- spinovestibular tract: C1-C4,neuromuscular spindles and Golgi tendon organs to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to Central Cervical Nucleus (N2) to Vestibular Nucleus
- spinothalamic tract (STT, conscious):
- spinocerebellar tracts (proprioceptive sensation, subconscious, very lateral slice):
- cuneocerebellar tract: C1-C7,proprioceptive/fine touch/vibration to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to Accessory Cuneate Nucleus (N2) to Cerebellum
- dorsal spinocerebellar tract, posterior spinocerebellar tract (PSCT): neuromuscular spindles and Golgi tendon organs (trunk and lower limb) to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to Clarke's Nucleus (N2) to (unilaterally) Cerebellum
- ventral spinocerebellar tract, anterior spinocerebellar tract, Gower's tract (ASCT): C8-L3,proprioceptive/fine touch/vibration (body, legs) to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to Intermediomedial Nucleus (N2) to (bilaterally in C8-L3) Cerebellum (to cortex and globose, emboliform nuclei)
- rostral spinocerebellar tract (RSCT): C8-L3,proprioceptive/fine touch/vibration (body, legs) to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to Centrobasalis Nucleus (N2) to Cerebellum (bilaterally)
- anterolateral system:
DESCENDING:

- dorsolateral tract, posterolateral tract
- Periaqueductal Gray Matter (N1) to
- RVM (Raphe Nucleus of Medulla, Gigantocellular Reticular Nucleus) (N2) to Marginal Nucleus (N3) (inhibit pain, serotonine)
- Barrington's Nucleus (N2) to Sacral Parasympathetic Nucleus, Onuf's Nucleus (N3) to colon, rectum, bladder, penis, vagina
- Ventral Tegmental Area (N1) to Substantia Gelatinosa (N2) (inhibit pain, dopamine, reward, placebo)
- Locus Coeruleus (N1) to Intermediolateral Nucleus (N2) (inhibit pain, norepinephrine - physiological responses to stress and panic)
- Periaqueductal Gray Matter (N1) to
- lateral motor tracts:
- lateral corticospinal tract (LCST, flexor motor, pyramidal tract, conscious, cervical-medial, thoracic, lumbar-lateral, distal muscles, decussating to contralateral and ipsilateral): cortex BA 1-4,6 (N1) to
- Retroposterolateral Nucleus (N2) to distal limb finger muscles
- Posterolateral Nucleus interneuron to motoneuron (N2-N3) to distal limb flexors muscles
- rubrospinal tract, tract of Monakow (flexor motor, upper limbs, subconscious): Red Nucleus (magnocellular neurons) (N1) to (mediation of voluntary movement by cerebelum):
- Retroposterolateral Nucleus (N2) to distal limb finger muscles
- Posterolateral Nucleus (N2) to distal limb flexors muscles
- solitariospinal tract: (subconscious motor tract, see http://www.slideshare.net/LawrenceJames/regulation-of-respiration, from corticobulbar, corticonuclear tract)
- Solitary Nucleus (autonomic respiration, start) (N1) to Ambiguus Nucleus, Retroambiguus Nucleus (expiratory cencer, active when forced breathing) (N2) to nucleus ambiguus (inspiratory center) (N3) to
- Phrenic Nucleus (N4) to diaphragm, intercostal nerves to intercostal muscles
- Parabrachial Nucleus (pacemaker, controls rate and pattern of breathing) (N1) to Ambiguus Nucleus (N2) to
- Phrenic Nucleus (N3) to diaphragm, intercostal nerves to intercostal muscles
- Solitary Nucleus (autonomic respiration, start) (N1) to Ambiguus Nucleus, Retroambiguus Nucleus (expiratory cencer, active when forced breathing) (N2) to nucleus ambiguus (inspiratory center) (N3) to
- lateral corticospinal tract (LCST, flexor motor, pyramidal tract, conscious, cervical-medial, thoracic, lumbar-lateral, distal muscles, decussating to contralateral and ipsilateral): cortex BA 1-4,6 (N1) to
- ventral motor tracts:
- ventral corticospinal tract, anterior/medial corticospinal tract, direct pyramidal tract, anterior cerebrospinal fasciculus (VCST, extensor motor, pyramidal tract, conscious, axial, proximal muscles, ipsilateral): cortex BA 1-4,6 (N1) to:
- Posteromedial Nucleus (N2) to axial muscles
- Phrenic Nucleus (N2) to diaphragm, intercostal nerves to intercostal muscles
- lateral vestibulospinal tract (LVST, flexor motor, anti-gravity muscles, lateral, inferior, trunk/legs extensors, arm flexors, subconscious): Vestibular Nucleus (giant cells of Deiters) (N1) to
- Ventromedial Nucleus (N2) to trunk and ipsilateral limbs
- Posterolateral Nucleus (N2) to arms, legs (modulates muscle tone to maintain equilibrium)
- tectospinal tract, colliculospinal tract (TST, flexor motor, reflex postural movementa - coordinate head, neck, and eye movements by visual and auditory stimuli): Deep Superior Colliculus (N1) to
- Spinal Accessory Nucleus (C1-C4) (N2) to axial muscles of neck
- Ciliospinal Center (N2) to Superior Cervical Ganglion (N3) to muscles of iris
- reticulospinal tract (RST, extensor motor, control by hypothalamus of sympathetic and sacral parasympathetic outflow, subconscious):
- medullary reticulospinal tract, lateral reticulospinal tract (LRST, flexor motor, inhibiting excitatory axial extensor muscles of movement, excite flexors):
- Gigantocellular Reticular Nucleus (N1) to Posterolateral Nucleus (N2) to distal muscles (exciting anti-gravity, inhibit stretch reflexes)
- Caudal Pontine Reticular Nucleus (N1) to Posteromedial Nucleus (N2) to axial muscles
- Oral Pontine Reticular Nucleus (N1) to Posteromedial Nucleus (N2) to axial muscles
- pontine reticulospinal tract, medial reticulospinal tract (MRST, extensor motor, facilitates flexor spinal reflexes):
- Medullary Reticular Formation (N1) to Ventrolateral Nucleus (N2) to distal muscles (extensor muscles)
- hypothalamospinal tract, oculosympathetic pathway (HTST, sympathetic motor): Paraventricular Nucleus (N1) to Ciliospinal Center (N2) to Superior Cervical Ganglion (N3) to dilator muscle of iris
- medullary reticulospinal tract, lateral reticulospinal tract (LRST, flexor motor, inhibiting excitatory axial extensor muscles of movement, excite flexors):
- medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF):
- medial vestibulospinal tract (MVST, extensor motor, subconscious):
- Vestibular Nucleus (medial) (N1) to
- Spinal Accessory Nucleus (N2) to neck muscles (ensures neck and trunk movements coordinated with eye movements)
- Abducens Nucleus to Oculomotor Nucleus to muscles of eye
- Oculomotor Nucleus to muscles of eye
- Trochlear Nucleus to muscles of eye
- Cajal Nucleus to Oculomotor Nucleus to muscles of eye
- Vestibular Nucleus (medial) (N1) to
- medial vestibulospinal tract (MVST, extensor motor, subconscious):
- ventral corticospinal tract, anterior/medial corticospinal tract, direct pyramidal tract, anterior cerebrospinal fasciculus (VCST, extensor motor, pyramidal tract, conscious, axial, proximal muscles, ipsilateral): cortex BA 1-4,6 (N1) to:
INTRASPINAL:
- A-alpha receptors to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to
- alpha motor neurons (N2) to the same agonist muscles (myotatic/stretch reflex to support increased load)
- Substantia Gelatinosa GABA interneurons (N2) to alpha motor neurons (N3) to antagonist muscles (reciprocal inhibition in stretch reflex)
- A-delta receptors to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to
- C receptors to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to Substantia Gelatinosa (interneurons) (N2) to
- viscerosensory information to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to Marginal Nucleus (N2) to Intermediolateral Nucleus (IML) to white rami (sympathetic tract, preganglionic fibers)
- Sacral Parasympathetic Nucleus to Onuf's Nucleus
- C fibers of intestine and bladder to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to Onuf's Nucleus (N3) to Sacral Parasympathetic Nucleus (N4) to
- Pelvic Peripheral Ganglion (bladder ganglion) (N5) to detrusor muscle of bladder (via pelvic nerve, excite bladder, relax uretra)
- colon, rectum
- A-delta/C sacral fibers to Dorsal Root Ganglion (N1) to Intermediolateral Nucleus (N2) to Dorsal Commissural Nucleus (N3) to
- hypogastric nerve
- Pelvic Peripheral Ganglion
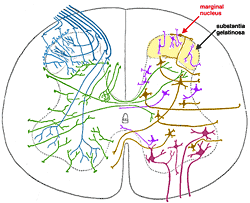
SENSORY NUCLEI CONNECTED TO SPINAL CORD
- Forebrain Telencephalon
- Somatosensory Cortex - sensory, fasciculus cuneatus/fasciculus gracilis/trigeminothalamic tract/anterior spinothalamic tract
- Posterior Insular Cortex - sensory, lateral spinothalamic tract
- Dorsal Anterior Cingulate Area - sensory, lateral spinothalamic tract
- Forebrain Diencephalon
- Hypothalamus
- Dorsomedial Hypothalamic Nucleus - sensory, spinohypothalamic tract
- Lateral Nucleus - sensory, spinohypothalamic tract
- Preoptic Area - sensory, spinohypothalamic tract
- Suprachiasmatic Nucleus - sensory, spinohypothalamic tract
- Supraoptic Nucleus - sensory, spinohypothalamic tract
- Thalamus
- Centromedian Nucleus of Thalamus - sensory, trigeminothalamic tract/spinoreticular tract
- Mediodorsal Nucleus of Thalamus - sensory, lateral spinothalamic tract
- Parafascicular Nucleus of Thalamus - sensory, trigeminothalamic tract
- Ventral Posteroinferior Nucleus - sensory, lateral spinothalamic tract
- Ventral Posterolateral Nucleus - sensory, fasciculus cuneatus/fasciculus gracilis/spinocervical tract/anterior spinothalamic tract
- Ventral Posteromedial Nucleus - sensory, fasciculus cuneatus/trigeminothalamic tract
- Hypothalamus
- Midbrain Mesencephalon
- Cuneiform Nucleus - sensory, spinoreticular tract
- Periaqueductal Gray Matter - sensory, spinocervical tract/spinomesencephalic tract
- Hindbrain Metencephalon
- Cerebellum - sensory, cuneocerebellar tract/dorsal spinocerebellar tract/ventral spinocerebellar tract/rostral spinocerebellar tract/spinoolivary tract
- Principal Trigeminal Nucleus - sensory, trigeminothalamic tract
- Hindbrain Myelencephalon
- Accessory Cuneate Nucleus - sensory, cuneocerebellar tract
- Cuneate Nucleus - sensory, tract of Lissauer/fasciculus cuneatus
- Gracile Nucleus - sensory, tract of Lissauer/fasciculus gracilis
- Inferior Olivary Nucleus - sensory, spinoolivary tract
- Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus - sensory, trigeminothalamic tract/trigeminothalamic tract
MOTOR NUCLEI CONNECTED TO SPINAL CORD
- Forebrain Telencephalon
- neocortex, BA 1-4,6 - motor, lateral corticospinal tract/ventral corticospinal tract
- Midbrain Mesencephalon
- Cajal Nucleus - motor, medial longitudinal fasciculus
- Oculomotor Nucleus - motor, medial longitudinal fasciculus
- Red Nucleus - motor, rubrospinal tract
- Trochlear Nucleus - motor, medial longitudinal fasciculus
- Ventral Tegmental Area - modulatory, dorsolateral fasciculus
- Hindbrain Metencephalon
- Abducens Nucleus - motor, medial longitudinal fasciculus
- Locus Coeruleus - modulatory, dorsolateral fasciculus
- Parabrachial Nucleus - motor, solitariospinal tract
- Hindbrain Myelencephalon
- Expiratory Center
- Ambiguus Nucleus - motor, solitariospinal tract
- Retroambiguus Nucleus - motor, solitariospinal tract
- Raphe Nucleus of Medulla - modulatory, dorsolateral fasciculus
- Expiratory Center
NUCLEI RECIPROCALLY CONNECTED TO SPINAL CORD
- Forebrain Diencephalon
- Hypothalamus
- Paraventricular Nucleus - sensory, spinohypothalamic tract; modulatory, hypothalamospinal tract
- Hypothalamus
- Midbrain Mesencephalon
- Deep Superior Colliculus - sensory, spinotectal tract; motor, tectospinal tract
- Hindbrain Metencephalon
- Barrington's Nucleus - sensory, dorsolateral fasciculus; motor, dorsolateral fasciculus
- Pontine Reticular Formation
- Gigantocellular Reticular Nucleus - sensory, spinoreticular tract; modulatory, dorsolateral fasciculus; motor, pontine reticulospinal tract
- Oral Pontine Reticular Nucleus - sensory, spinoreticular tract; motor, pontine reticulospinal tract
- Caudal Pontine Reticular Nucleus - sensory, spinoreticular tract; motor, pontine reticulospinal tract
- Vestibular Nucleus - sensory, spinovestibular tract; motor/modulatory, medial longitudinal fasciculus/lateral vestibulospinal tract/medial vestibulospinal tract
- Hindbrain Myelencephalon
- Medullary Reticular Formation - sensory, spinoreticular tract; motor, medullary reticulospinal tract
- Solitary Nucleus - sensory, spinosolitary tract; motor, solitariospinal tract
GANGLIA CONNECTED TO SPINAL CORD
- Dorsal Root Ganglion (DRG): sensory, all tracts except medial longitudinal fasciculus/trigeminothalamic tract; A-alpha-Ia/A-alpha-Ib/A-beta/A-delta/C sensory data
- Inferior Mesenteric Ganglion (IMG): motor, sympathetic
- Jugular Ganglion (JUG): sensory, trigeminothalamic tract; A-beta/A-delta/C sensory data
- Nodose Ganglion (NDG): sensory, trigeminothalamic tract; A-beta/A-delta/C sensory data
- Pelvic Peripheral Ganglion: intraspinal; B/C motor data
- Superior Cervical Ganglion (SCG): motor, tectospinal tract; modulatory, hypothalamospinal tract; B/C motor data
- Trigeminal Ganglion (TRG): sensory, trigeminothalamic tract; A-alpha-Ia/A-alpha-Ib/A-beta/A-delta/C sensory data
FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
SENSORY NUCLEI FROM DRG TO VPL/VPM

- DRG -> Cuneate Nucleus -> VPL - upper body
- DRG -> Gracile Nucleus -> VPL - lower body
- DRG -> Principal Trigeminal Nucleus -> VPM - head and face
SENSORY NUCLEI FROM SPINAL CORD TO VPL/VPM
- DRG -> Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus -> VPM - head and face deep pain/temperature
- DRG -> Marginal Nucleus -> VPL - fast pain/temperature
- DRG -> Substantia Gelatinosa -> VPL - slow pain/temperature
SENSORY NUCLEI FROM SPINAL CORD TO CR
- DRG.CX -> Accessory Cuneate Nucleus -> CR - upper extremity (to C7)
- DRG.TX,LX -> Clarke's Nucleus -> CR - from C8
INTERSPINAL SENSORY TO MOTOR
- vessel/gland (GVA) -> DRG -> Substantia Gelatinosa -> Intermediolateral Nucleus -> (GVE) vessel/gland
- muscle (GSA) -> DRG -> Posteromedial Nucleus/Ventromedial Nucleus/Posterolateral Nucleus/Ventrolateral Nucleus -> (GSE) muscle
- muscle (GSA) -> DRG -> Substantia Gelatinosa -> Posteromedial Nucleus/Ventromedial Nucleus/Posterolateral Nucleus/Ventrolateral Nucleus -> (GSE) muscle