Difference between revisions of "SpinalCordTracts"
From aHuman Wiki
(Automated page entry using MWPush.pl) |
(Automated page entry using MWPush.pl) |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
* TRACT SLS: '''spinolimbic system'''; connect spinal cord with limbic structures | * TRACT SLS: '''spinolimbic system'''; connect spinal cord with limbic structures | ||
** [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8613771 TRACT SHTT]: '''spinohypothalamic tract'''; provide nociceptive information to a variety of nuclei throughout the diencephalon and brainstem bilaterally (nociception integration, from C-fibers innervating muscles); path: {body pain, temperature} -> {hypothalamus} | ** [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8613771 TRACT SHTT]: '''spinohypothalamic tract'''; provide nociceptive information to a variety of nuclei throughout the diencephalon and brainstem bilaterally (nociception integration, from C-fibers innervating muscles); path: {body pain, temperature} -> {hypothalamus} | ||
| − | *** <img src="http://ahuman. | + | *** <img src="http://usvn.ahuman.org/svn/ahwiki/images/wiki/research/biomodel/spinohypothalamic-tract.png" height=600> |
*** path '''SHT.HT.AHT''': affect appetite, autonomic and homeostatic functions, and related motivational and affective responses to autonomic function (pain fibers to anterior hypothalamus); FIBERS={C-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: [[BrainRegionBMA_SC_LH_LSN|Lateral Spinal Nucleus,BMA.SC.LH.LSN]] -> [[BrainRegionHTA_FD_HT_AH|Anterior Hypothalamic Nucleus,HTA.FD.HT.AH]] | *** path '''SHT.HT.AHT''': affect appetite, autonomic and homeostatic functions, and related motivational and affective responses to autonomic function (pain fibers to anterior hypothalamus); FIBERS={C-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: [[BrainRegionBMA_SC_LH_LSN|Lateral Spinal Nucleus,BMA.SC.LH.LSN]] -> [[BrainRegionHTA_FD_HT_AH|Anterior Hypothalamic Nucleus,HTA.FD.HT.AH]] | ||
*** path '''SHT.HT.DM''': affect blood pressure, heart rate (pain fibers to dorsomedial nucleus); FIBERS={C-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: [[BrainRegionBMA_SC_LH_LSN|Lateral Spinal Nucleus,BMA.SC.LH.LSN]] -> [[BrainRegionHTA_FD_HT_DM|Dorsomedial Hypothalamic Nucleus,HTA.FD.HT.DM]] | *** path '''SHT.HT.DM''': affect blood pressure, heart rate (pain fibers to dorsomedial nucleus); FIBERS={C-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: [[BrainRegionBMA_SC_LH_LSN|Lateral Spinal Nucleus,BMA.SC.LH.LSN]] -> [[BrainRegionHTA_FD_HT_DM|Dorsomedial Hypothalamic Nucleus,HTA.FD.HT.DM]] | ||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
** [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spinocerebellar_tract TRACT SCS]: '''spinocerebellar system'''; spinal cord to cerebellum | ** [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spinocerebellar_tract TRACT SCS]: '''spinocerebellar system'''; spinal cord to cerebellum | ||
* TRACT DSCS: '''direct spinocerebellar system'''; spinal cord nuclei to cerebellum (lower are dorsal and ventral SC tracts; upper are cuneocerebellar and rostral spinocerebellar tract) | * TRACT DSCS: '''direct spinocerebellar system'''; spinal cord nuclei to cerebellum (lower are dorsal and ventral SC tracts; upper are cuneocerebellar and rostral spinocerebellar tract) | ||
| − | ** <img src="http://ahuman. | + | ** <img src="http://usvn.ahuman.org/svn/ahwiki/images/wiki/research/biomodel/spinocerebellar-tracts.png" height=600> |
** [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Posterior_external_arcuate_fibers TRACT CSCT]: '''cuneocerebellar tract'''; relay information about limb position and movement to the cerebellum (upper extremity equivalent of Clarkes column to CR tract - posterior spinocerebellar tract); path: {proprioceptive/fine touch/vibration, C1-C7} -> {cerebellum, vermis and paravermis of the ipsilateral posterior lobe} | ** [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Posterior_external_arcuate_fibers TRACT CSCT]: '''cuneocerebellar tract'''; relay information about limb position and movement to the cerebellum (upper extremity equivalent of Clarkes column to CR tract - posterior spinocerebellar tract); path: {proprioceptive/fine touch/vibration, C1-C7} -> {cerebellum, vermis and paravermis of the ipsilateral posterior lobe} | ||
*** <img src="http://what-when-how.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/04/tmp14100_thumb.jpg"> | *** <img src="http://what-when-how.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/04/tmp14100_thumb.jpg"> | ||
| Line 133: | Line 133: | ||
* [https://www.dartmouth.edu/~rswenson/NeuroSci/chapter_8A.html TRACT BSS]: '''corticobulbospinal system'''; pattern locomotion, inhibit reflex activity in spinal cord | * [https://www.dartmouth.edu/~rswenson/NeuroSci/chapter_8A.html TRACT BSS]: '''corticobulbospinal system'''; pattern locomotion, inhibit reflex activity in spinal cord | ||
** [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corticobulbar_tract TRACT CBT]: '''corticobulbar tract'''; carrying the motor function of the non-oculomotor cranial nerves (V, VII, XI, and XII; indirectly - via IX and X in nucleus ambiguus) | ** [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corticobulbar_tract TRACT CBT]: '''corticobulbar tract'''; carrying the motor function of the non-oculomotor cranial nerves (V, VII, XI, and XII; indirectly - via IX and X in nucleus ambiguus) | ||
| − | *** <img src="http://ahuman. | + | *** <img src="http://usvn.ahuman.org/svn/ahwiki/images/wiki/research/biomodel/spinobulbar.jpg" height=800> |
** [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rubrospinal_tract TRACT RBST]: '''rubrospinal tract'''; mediation of voluntary movement, upper limbs; control of flexor tone (extrapyramidal; activates flexors, inhibits extensors) | ** [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rubrospinal_tract TRACT RBST]: '''rubrospinal tract'''; mediation of voluntary movement, upper limbs; control of flexor tone (extrapyramidal; activates flexors, inhibits extensors) | ||
*** <img src="http://www.neuroanatomy.wisc.edu/virtualbrain/Images/22B.jpg" height=600> | *** <img src="http://www.neuroanatomy.wisc.edu/virtualbrain/Images/22B.jpg" height=600> | ||
* [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lateral_corticospinal_tract TRACT ASTT]: '''lateral corticospinal tract'''; flexor motor, pyramidal tract, conscious; volitional skilled motor activity (90 percents of corticospinal fibers; 80 percents - contrallateral; 10 percents - unilateral; cervical-medial, thoracic, lumbar-lateral, distal muscles, decussating to contralateral and ipsilateral); path: {cortex BA 1-4,6} -> {muscle groups that require concentration and conscious thought to control; upper limb digits} | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lateral_corticospinal_tract TRACT ASTT]: '''lateral corticospinal tract'''; flexor motor, pyramidal tract, conscious; volitional skilled motor activity (90 percents of corticospinal fibers; 80 percents - contrallateral; 10 percents - unilateral; cervical-medial, thoracic, lumbar-lateral, distal muscles, decussating to contralateral and ipsilateral); path: {cortex BA 1-4,6} -> {muscle groups that require concentration and conscious thought to control; upper limb digits} | ||
** <img src="http://www.ib.cnea.gov.ar/~redneu/2013/BOOKS/Principles%20of%20Neural%20Science%20-%20Kandel/gateway.ut.ovid.com/fulltextservice/ct%7B06b9ee1beed594190674f1983457a7dd32af6a0d5a4c9892~23/da4c18ff8.gif.png" height=800> | ** <img src="http://www.ib.cnea.gov.ar/~redneu/2013/BOOKS/Principles%20of%20Neural%20Science%20-%20Kandel/gateway.ut.ovid.com/fulltextservice/ct%7B06b9ee1beed594190674f1983457a7dd32af6a0d5a4c9892~23/da4c18ff8.gif.png" height=800> | ||
Revision as of 13:01, 21 June 2015
Spinal Cord
Home -> BiologicalLifeResearch -> SpinalCord -> SpinalCordTracts
This page is intended to list all neural tracts related to spinal cord.
SPINAL CORD TRACTS
(generated)
TRACT SET: Ascending Tracts

- TRACT ALS: anterolateral system; conveys pain, temperature (protopathic sensation), and crude touch from the periphery to the brain
- TRACT PSTS: paleospinothalamic system; transmits pain mainly from the peripheral slow-chronic type C pain fibers; transmits information to thalamus about pain, temperature, itch and crude touch (conscious; cervical-anterior-toward-contralateral, thoracic, lumbar, sacral-lateral slices)
- TRACT ASTT: anterior spinothalamic tract (anterolateral tract); pain, temperature, light touch (tactile sensibility), two-point discrimination, stereognosis; path: {skin - slow pain, temperature, slightly tactile} -> {BA 3,1,2}
-

- path ASTT: slightly tactile (head and body MD,MC,PC,HF receptors to S1); FIBERS={C-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Dorsal Root Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.DRG -> Substantia Gelatinosa,BMA.SC.PH.SG -> Ventral Posterolateral Nucleus,SMA.FD.TH.VPL -> Somatosensory Cortex,SMA.NC.PG.S1
-
- TRACT LSTT: lateral spinothalamic tract; pain, temperature; path: {body pain, temperature, crude touch} -> {BA 3,1,2}
-

- path LSTT: pain, temperature (head and body FN,RC receptors to marginal nucleus); FIBERS={A-delta-sensory}, ENDINGS={SAD}: Dorsal Root Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.DRG -> Marginal Nucleus,BMA.SC.PH.MG
- path LSTT.MD: pain, temperature for reward (pain to frontal lobe); FIBERS={C-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Substantia Gelatinosa,BMA.SC.PH.SG -> Mediodorsal Nucleus of Thalamus,FCA.FD.TH.MD -> Dorsal Anterior Cingulate Area,CGA.NC.DACG
- path LSTT.VPI: pain, temperature for emotion (pain to insula); FIBERS={A-delta-sensory}, ENDINGS={SAD}: Marginal Nucleus,BMA.SC.PH.MG -> Ventral Posteroinferior Nucleus,SMA.FD.TH.VPI -> Posterior Insular Cortex,PHA.NC.INS.PIC
-
- TRACT LST: tract of Lissauer (fasciculus of Lissauer, tract/zone of Lissauer, dorsolateral fasciculus, posterolateract tract, dorsolateral tract); fast pain; intraspinal, discriminative pain and temperature information - location, intensity and quality (pain duration equals to stimulus duration; joins spinothalamic tract); path: {A-delta pain fibers} -> {to neocortex BA 3b}
- path DLF: autonomic and homeostatic functions, initial sharp localization of pain (body to hypothalamus and neocortex); FIBERS={A-delta-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Dorsal Root Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.DRG -> Marginal Nucleus,BMA.SC.PH.MG -> Lateral Spinal Nucleus,BMA.SC.LH.LSN
- path DLF.VPL: from medial LSN; joins fasciculus gracilis; initial sharp localization of pain (lower body to neocortex BA 3b); FIBERS={A-delta-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Lateral Spinal Nucleus,BMA.SC.LH.LSN -> Gracile Nucleus,BMA.HM.GR -> Ventral Posterolateral Nucleus,SMA.FD.TH.VPL -> Somatosensory Cortex,SMA.NC.PG.S1
- path DLF.VPM: from lateral LSN; joins fasciculus cuneatus; initial sharp localization of pain (upper body to neocortex BA 3b); FIBERS={A-delta-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Lateral Spinal Nucleus,BMA.SC.LH.LSN -> Cuneate Nucleus,BMA.HM.CU -> Ventral Posteromedial Nucleus,SMA.FD.TH.VPM -> Somatosensory Cortex,SMA.NC.PG.S1
- TRACT ASTT: anterior spinothalamic tract (anterolateral tract); pain, temperature, light touch (tactile sensibility), two-point discrimination, stereognosis; path: {skin - slow pain, temperature, slightly tactile} -> {BA 3,1,2}
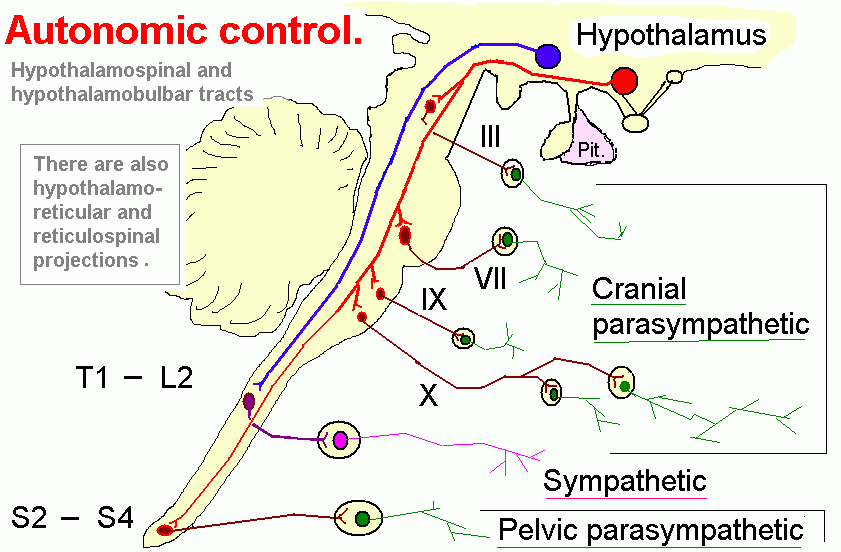
- TRACT SLS: spinolimbic system; connect spinal cord with limbic structures
- TRACT SHTT: spinohypothalamic tract; provide nociceptive information to a variety of nuclei throughout the diencephalon and brainstem bilaterally (nociception integration, from C-fibers innervating muscles); path: {body pain, temperature} -> {hypothalamus}
-

- path SHT.HT.AHT: affect appetite, autonomic and homeostatic functions, and related motivational and affective responses to autonomic function (pain fibers to anterior hypothalamus); FIBERS={C-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Lateral Spinal Nucleus,BMA.SC.LH.LSN -> Anterior Hypothalamic Nucleus,HTA.FD.HT.AH
- path SHT.HT.DM: affect blood pressure, heart rate (pain fibers to dorsomedial nucleus); FIBERS={C-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Lateral Spinal Nucleus,BMA.SC.LH.LSN -> Dorsomedial Hypothalamic Nucleus,HTA.FD.HT.DM
- path SHT.HT.LT: affect thirst and hunger (pain fibers to lateral nucleus); FIBERS={C-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Lateral Spinal Nucleus,BMA.SC.LH.LSN -> Lateral Nucleus,HTA.FD.HT.LT
- path SHT.HT.SCN: affect 24-hour rhythms (pain fibers to anterior hypothalamus); FIBERS={C-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Lateral Spinal Nucleus,BMA.SC.LH.LSN -> Suprachiasmatic Nucleus,HTA.FD.HT.SCN
- path SHT.HT.SO: affect blood volume or blood pressure (pain fibers to anterior hypothalamus); FIBERS={C-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Lateral Spinal Nucleus,BMA.SC.LH.LSN -> Supraoptic Nucleus,HTA.FD.HT.SO
- path SHT.LSN: pain, temperature for ANS (pain fibers to spinal integrator LSN); FIBERS={C-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Dorsal Root Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.DRG -> Lateral Spinal Nucleus,BMA.SC.LH.LSN
-
- TRACT SMST: spinomesencephalic tract; ascending pain and temperature fibers of the spinothalamic tract also send information to the PAG; path: {MG nucleus} -> {PAG, MRF}
-

- path SMT.PAG: initiates pain inhibition (activates enkephalin-releasing neurons that project to raphe nuclei, descending to inhibitory interneurons located in Laminae II); FIBERS={A-delta-sensory}, ENDINGS={SAD}: Dorsal Root Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.DRG -> Marginal Nucleus,BMA.SC.PH.MG -> Periaqueductal Gray Matter,FBA.MM.PAG
-
- TRACT SST: spinosolitary tract; central transmission of visceronoceptive messages (visceronociception, short-latency nociceptive input); path: {body pain, temperature} -> {solitary nucleus}
- path SST: autonomic regulation of of stress response to painful visceral stimuli (pain fibers to solitary nucleus to parabrachial nucleus); FIBERS={C-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Lateral Spinal Nucleus,BMA.SC.LH.LSN -> Solitary Nucleus,HMA.HM.SOL -> Parabrachial Nucleus,BMA.HP.PB
- path SST.LSN: pain, temperature for ANS (pain fibers to spinal integrator LSN); FIBERS={C-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Dorsal Root Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.DRG -> Lateral Spinal Nucleus,BMA.SC.LH.LSN
- TRACT SHTT: spinohypothalamic tract; provide nociceptive information to a variety of nuclei throughout the diencephalon and brainstem bilaterally (nociception integration, from C-fibers innervating muscles); path: {body pain, temperature} -> {hypothalamus}
- TRACT SRS: spinoreticular system; automatic responses to pain
- TRACT SMRT: spinomedulloreticular tract; automatic responses to pain; path: {visceral pain} -> {MRF, entire cortex}
-
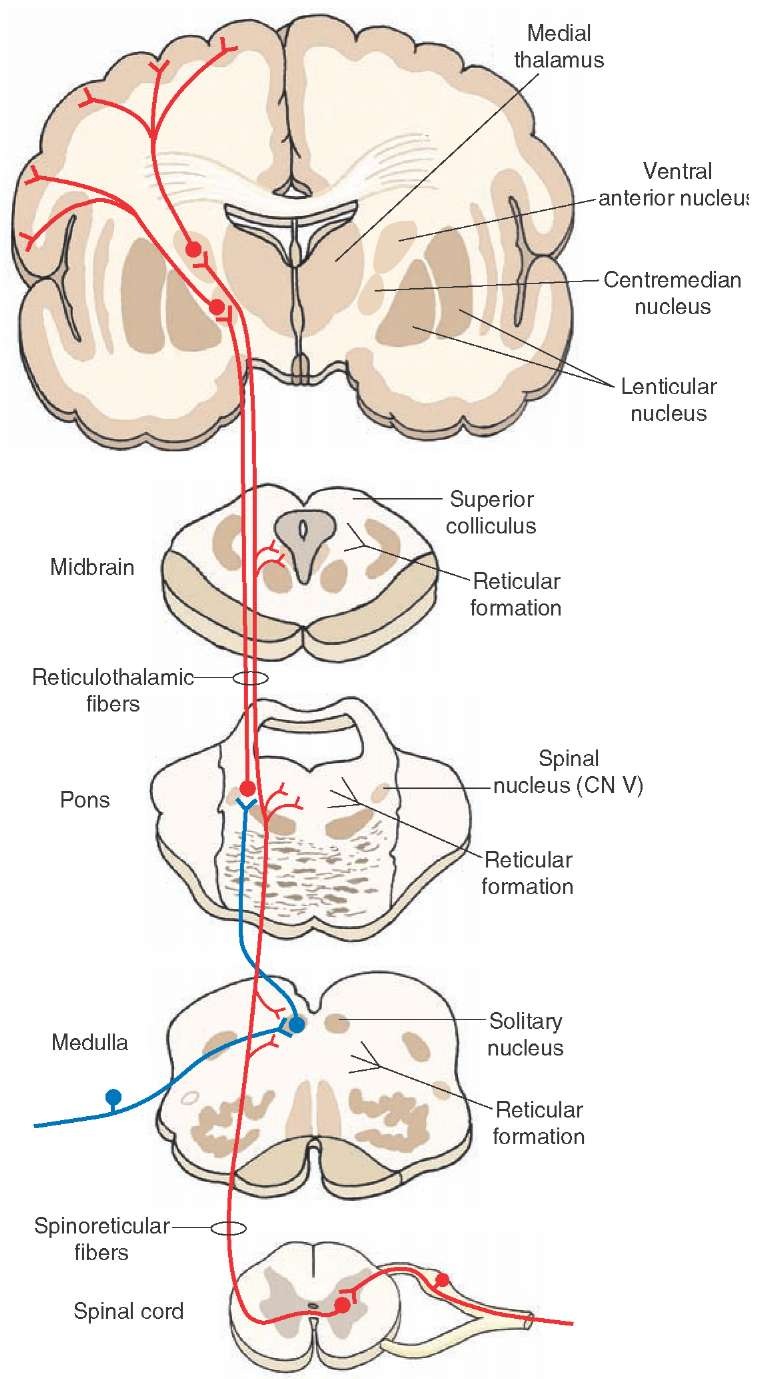
- path SRT.MED: automatic responses to pain; attentional and alerting mechanisms (viceral pain to spinal cord to medullary reticular formation; visceral and somatic pain to MRF); FIBERS={A-delta-sensory}, ENDINGS={SAD}: Dorsal Root Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.DRG -> Intermediomedial Nucleus,AVA.SC.IZ.IMM -> Medullary Reticular Formation,MBA.HM.RF.MED
-
- TRACT SPRT: spinopontoreticular tract; automatic responses to pain; path: {visceral pain} -> {MRF, entire cortex}
-

- path SRT.VA: exerts excitatory influence predominantly on pontine reticular nuclei to facilitate contraction of extensor muscles of limb and trunk (crude touch/vibration to spinal cord to pontine reticular formation to thalamus; utilizes four levels of neurons); FIBERS={A-delta-sensory}, ENDINGS={SPC}: Dorsal Root Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.DRG -> Intermediomedial Nucleus,AVA.SC.IZ.IMM -> Medial Pontine Reticular Formation,HP.PRF.MPRF (Oral Pontine Reticular Nucleus,HMA.HP.PRF.RPO, Caudal Pontine Reticular Nucleus,HMA.HP.PRF.CRF, Pontine Reticulotegmental Nucleus,HMA.HP.PRF.PDT) -> Ventral Anterior Nucleus,MCA.FD.TH.VA
-
- TRACT STCT: spinotectal tract; spinovisual reflexes; head/eye movement toward stimulus source (arises in the anterolateral column); path: {free nerve endings; crude touch, temperature, pain} -> {inferior and superior colliculi}
- path STCT: Head and eye attention to non-visual stimuli (crude touch to nucleus proprius to superior colliculus); FIBERS={C-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Dorsal Root Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.DRG -> Proprius Nucleus,BMA.SC.PH.NP -> Deep Superior Colliculus,MBA.MM.SC.DEEP
- TRACT SMRT: spinomedulloreticular tract; automatic responses to pain; path: {visceral pain} -> {MRF, entire cortex}
- TRACT TTS: trigeminothalamic system (neospinothalamic tract); all somatosensory submodalities from head
-

- TRACT ATTT: anterior trigeminothalamic tract (ventral trigeminothalamic tract); awareness of the exact location of the painful stimulus; pain, temperature, and crude touch pathway; path: {face, head and neck} -> {SI - BA 1,2}
- path TTT.GNG: nociceptors (nociceptors of cranial nerves VII to spinal trigeminal nucleus); FIBERS={A-delta-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Geniculate Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.GNG -> Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus,HMA.HM.TGM.STR
- path TTT.JUG: nociceptors (nociceptors of cranial nerves IX,X to spinal trigeminal nucleus); FIBERS={A-delta-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Jugular Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.JUG -> Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus,HMA.HM.TGM.STR
- path TTT.NOD: nociceptors (nociceptors of cranial nerves X to spinal trigeminal nucleus); FIBERS={A-delta-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Nodose Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.NOD -> Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus,HMA.HM.TGM.STR
- path TTT.TRG: nociceptors (head, face and intraoral structures nociceptors to spinal trigeminal nucleus); FIBERS={A-delta-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Trigeminal Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.TRG -> Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus,HMA.HM.TGM.STR
- path TTT.VPM: nociceptors (spinal trigeminal nucleus to S1); FIBERS={A-delta-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus,HMA.HM.TGM.STR -> Ventral Posteromedial Nucleus,SMA.FD.TH.VPM -> Somatosensory Cortex,SMA.NC.PG.S1
- TRACT DTTT: dorsal trigeminal tract (dorsal trigeminothalamic tract, lemniscus); immediate awareness of a painful sensation; pressure and tactile discrimination sensation; path: {head MC,PC} -> {SII - BA 40,43}
- path DTT: face dull, burning pain, deep, aching pain, temperature and crude touch (head, face and intraoral structures to Precentral Cortex); FIBERS={C-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Trigeminal Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.TRG -> Principal Trigeminal Nucleus,HMA.HP.PTP.PTR
- path DTT.MD: pain, temperature for reward (marginal nucleus to frontal lobe); FIBERS={C-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Principal Trigeminal Nucleus,HMA.HP.PTP.PTR -> Mediodorsal Nucleus of Thalamus,FCA.FD.TH.MD -> Dorsal Anterior Cingulate Area,CGA.NC.DACG
- path DTT.PF: face dull, burning pain, deep, aching pain, temperature and crude touch (head, face and intraoral structures to Precentral Cortex); FIBERS={C-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Principal Trigeminal Nucleus,HMA.HP.PTP.PTR -> Parafascicular Nucleus of Thalamus,BGA.FD.TH.PF -> Precentral Cortex,SMA.NC.PO.PCC
- path DTT.VPI: pain, temperature for emotion (marginal nucleus to insula); FIBERS={C-sensory}, ENDINGS={SFN}: Principal Trigeminal Nucleus,HMA.HP.PTP.PTR -> Ventral Posteroinferior Nucleus,SMA.FD.TH.VPI -> Posterior Insular Cortex,PHA.NC.INS.PIC
- TRACT MLS: medial lemniscus system; transmits touch, vibration sense, proprioception data
-
-

- TRACT PCS: posterior column system (dorsal column, Reils band, Reils ribbon); two point discrimination (fine touch, fine pressure - MC), pressure (deep receptors - PC), vibration (PC), conscious proprioception (MS) (alpha/beta mechanoreceptors, conscious; discrimination of those sensations that an animal must explore actively)
-

- TRACT FCT: fasciculus cuneatus tract (tract of Burdach); upper body well-localized discriminative proprioception, fine touch (muscle afferents and cutaneous mechanoreceptors (C1-T6 dermatomes); thoracic-toward-contralateral and cervical slices); path: {upper trunk, forelimb deep structures and skin} -> {neocortex BA 3b, lateral}
- path PCT.CUL: conscious sensations of neck, trunk, and extremities (neck (C4), trunk (T1-T6), and extremities - arms (C5-T2) to S1 lateral); FIBERS={A-beta}, ENDINGS={SMC,SPC,SHF}: Dorsal Root Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.DRG -> Cuneate Nucleus,BMA.HM.CU -> Ventral Posterolateral Nucleus,SMA.FD.TH.VPL -> Somatosensory Cortex,SMA.NC.PG.S1
- path PCT.CUM: conscious sensations of head (geniohyoid (C1), head top (C2), head back above neck (C3) to S1 medial); FIBERS={A-alpha-Ia; A-beta}, ENDINGS={SMC,SPC,SHF}: Dorsal Root Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.DRG -> Cuneate Nucleus,BMA.HM.CU -> Ventral Posteromedial Nucleus,SMA.FD.TH.VPM -> Somatosensory Cortex,SMA.NC.PG.S1
- TRACT FGT: fasciculus gracilis tract (tract of Goll); lower body well-localized discriminative fine touch (sacral-toward-contralateral and lumbar slices; mostly cutaneous (proprioception via CLN)); path: {lower body, muscle afferents} -> {somatosensory cortex}
- path PCT.GRL: epicritic, kinesthetic, and conscious proprioceptive information from lower body (receptors of thoracic and lower limbs, T7-CX to neocortex BA 3b, medial); FIBERS={A-beta}, ENDINGS={SMS,SPC}: Dorsal Root Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.DRG -> Gracile Nucleus,BMA.HM.GR -> Ventral Posterolateral Nucleus,SMA.FD.TH.VPL -> Somatosensory Cortex,SMA.NC.PG.S1
-
- TRACT SCVT: spinocervical tract (Morin's tract); static position, Ruffini endings (thoracic-toward-contralateral and cervical slices); path: {receptors of thoracic and lower limbs, T7-CX} -> {somatosensory cortex}
-

- path SCVT: tactile/pressure pathway from the spinal cord to sensory cortex (tactile/pressure to S1); FIBERS={A-alpha; A-beta}, ENDINGS={SRC}: Dorsal Root Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.DRG -> Proprius Nucleus,BMA.SC.PH.NP -> Lateral Cervical Nucleus,BMA.SC.LH.LCV
- path SCVT.PAG: alerts about presence of cutaneous stimuli that might represent danger, necessitating flight (cutaneous stimuli to PAG); FIBERS={A-alpha; A-beta}, ENDINGS={SRC}: Lateral Cervical Nucleus,BMA.SC.LH.LCV -> Periaqueductal Gray Matter,FBA.MM.PAG
- path SCVT.VPL: four-neuron, fast-conducting, tactile/pressure pathway from the spinal cord to sensory cortex (tactile/pressure to S1); FIBERS={A-alpha; A-beta}, ENDINGS={SRC}: Lateral Cervical Nucleus,BMA.SC.LH.LCV -> Ventral Posterolateral Nucleus,SMA.FD.TH.VPL -> Somatosensory Cortex,SMA.NC.PG.S1
- TRACT SCS: spinocerebellar system; spinal cord to cerebellum
-
- TRACT DSCS: direct spinocerebellar system; spinal cord nuclei to cerebellum (lower are dorsal and ventral SC tracts; upper are cuneocerebellar and rostral spinocerebellar tract)
-

- TRACT CSCT: cuneocerebellar tract; relay information about limb position and movement to the cerebellum (upper extremity equivalent of Clarkes column to CR tract - posterior spinocerebellar tract); path: {proprioceptive/fine touch/vibration, C1-C7} -> {cerebellum, vermis and paravermis of the ipsilateral posterior lobe}
-

- path CSCT: proprioceptive and exteroceptive information (upper limb muscles to accessory cuneate nucleus to cerebellum); FIBERS={A-alpha-Ib-sensory; A-beta-sensory}, ENDINGS={SMS,SGT,SRC,SMD}: Dorsal Root Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.DRG -> Accessory Cuneate Nucleus,BMA.HM.ACU -> Cerebellum,MBA.HP.CR
-
- TRACT DSCT: dorsal spinocerebellar tract (posterior spinocerebellar tract, Flechsigs tract); conveys proprioceptive information from proprioceptors in the skeletal muscles and joints to the cerebellum (ipsilateral, proprioceptive and tactile information); path: {neuromuscular spindles and Golgi tendon organs, joint receptors, cutaneous receptors, lower limbs, below L3} -> {cerebellum, mainly ipsilateral anterior lobe}
- path DSCT: proprioceptive and exteroceptive information (lower limb muscles to clarkes nucleus to cerebellum); FIBERS={A-alpha-Ib-sensory; A-beta-sensory}, ENDINGS={SMS,SGT,SRC,SMD}: Dorsal Root Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.DRG -> Clarke Nucleus,BMA.SC.PH.CL -> Cerebellum,MBA.HP.CR
- TRACT RSCT: rostral spinocerebellar tract; transmits information from the golgi tendon organs of the cranial half of the body to the cerebellum (upper extremity equivalent of ventral spinocerebellar tract); path: {proprioceptive/fine touch/vibration, C1-C7} -> {cerebellum, anterior lobe}
-

- path RSCT: proprioceptive information (upper limb muscles to centrobasalis nucleus to cerebellum); FIBERS={A-alpha-Ib-sensory}, ENDINGS={SGT}: Dorsal Root Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.DRG -> Central Cervical Nucleus,BMA.SC.IZ.CCV -> Cerebellum,MBA.HP.CR
-
- TRACT VSCT: ventral spinocerebellar tract (anterior spinocerebellar tract, Gowers tract); conveys information about postural stability of the lower limbs to cerebellum (bilaterally, double cross, proprioceptive/fine touch/vibration); path: {neuromuscular spindles and Golgi tendon organs, trunk, C8-L3} -> {cerebellum}
-
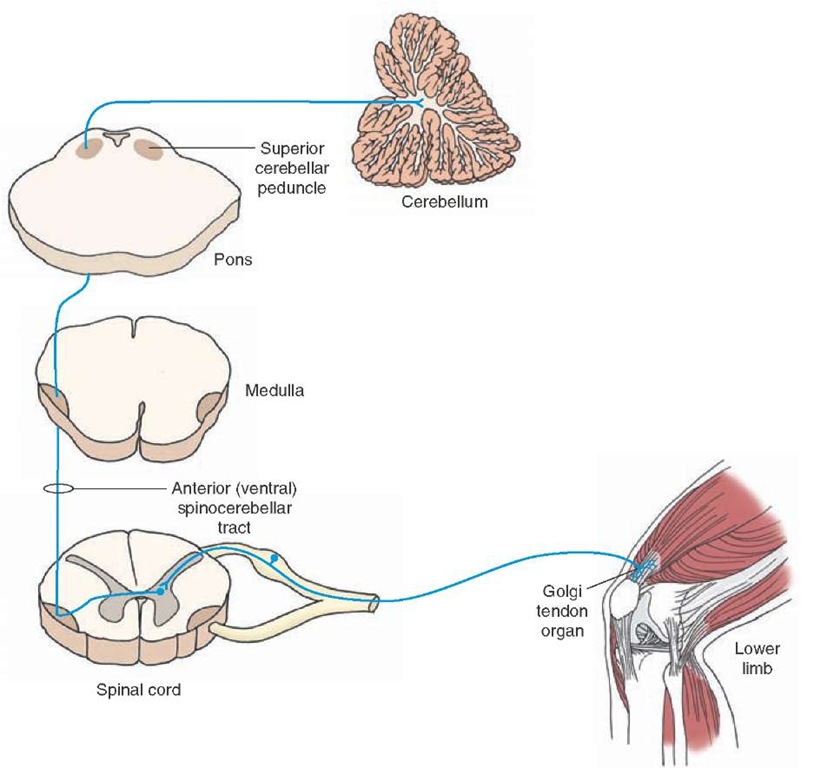
- path VSCT: proprioceptive information (body muscles to intermediomedial nucleus to cerebellum); FIBERS={A-alpha-Ib-sensory}, ENDINGS={SMS,SGT}: Dorsal Root Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.DRG -> Intermediomedial Nucleus,AVA.SC.IZ.IMM -> Cerebellum,MBA.HP.CR
-
-
- TRACT SMTS: spinometencephalic system; spinal cord to intermediate nucleus to cerebellum
-

- TRACT SOT: spinoolivary tract (Helwegs tract); automatic movements of head, neck upper limb; path: {proprioception information from muscles and tendons, cutaneous impulses} -> {cerebellum}
- path SOT.CCV: cutaneous information to cerebellum (skin mechanoreceptors to inferior olivary nucleus to cerebellum); FIBERS={A-alpha-Ia-sensory}, ENDINGS={SMC,SMD}: Dorsal Root Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.DRG -> Central Cervical Nucleus,BMA.SC.IZ.CCV -> Inferior Olivary Nucleus,BMA.HM.IO -> Cerebellum,MBA.HP.CR
- path SOT.NPR: proprioception to cerebellum (muscle spindles and Golgi tendons to inferior olivary nucleus to cerebellum); FIBERS={A-alpha-Ib-sensory}, ENDINGS={SGT,SMS}: Dorsal Root Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.DRG -> Proprius Nucleus,BMA.SC.PH.NP -> Inferior Olivary Nucleus,BMA.HM.IO -> Cerebellum,MBA.HP.CR
- TRACT SVT: spinovestibular tract; information from cutaneous and proprioceptive organs to CR; path: {proprioception information from muscles and tendons, cutaneous impulses} -> {cerebellum}
- path SVT.CCV: cutaneous information to cerebellum (skin mechanoreceptors to vestibular nucleus to cerebellum; C1-C4); FIBERS={A-alpha-Ia-sensory}, ENDINGS={SMC,SMD}: Dorsal Root Ganglion,AVA.PN.SG.DRG -> Central Cervical Nucleus,BMA.SC.IZ.CCV -> Vestibular Nucleus,BMA.HP.VB -> Cerebellum,MBA.HP.CR
-
TRACT SET: Descending Tracts

- TRACT ATS: autonomic tracts system (descending autonomic fibers); directs activity of glands, smooth muscles, and cardiac muscle; path: {cortex, HT, AM, RF} -> {sympathetic and parasympathetic}
- TRACT HTST: hypothalamospinal tract; control autonomic components (descend in dorsolateral funiculus; oculosympathetic pathway; next to superior cervical ganglion to common carotid - internal carotid - long ciliary nerves to pupillary dilator); path: {paraventrical nucleus of hypothalamus} -> {IML, sympathetic and parasympathetic preganglionic neurons; ciliospinal center of IML (T1,T2)}
-
- TRACT SSS: solitariospinal system; autonomic control of breathing (respiratory, vomiting and micturition functions); path: {ventrolateral solitary nucleus, retroambiguus nucleus} -> {diaphragm}
-

- TRACT SSET: solitariospinal expiratory tract; facilitate expiratory motor neurons to intercostal muscles (nucleus ambiguus - cranial division innervates muscles of the ipsilateral accessory muscles of respiration, principally via the vagus; nucleus retroambiguus - caudal division provides inspiratory and expiratory drive to the motor neurones of the intercostal muscles); path: {parabrachial nucleus to nucleus ambiguus, nucleus retroambiguus} -> {internal intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles}
-
- TRACT SSIT: solitariospinal inpiratory tract; facilitate inspiratory motor neurons in phrenic nucleus (neck muscles, external intercostal muscles - conscious forced inspiration; pneumotaxic center = medial parabrachial nucleus + kolliker-fuse nucleus, breathing frequency); path: {kolliker-fuse nucleus, receptors to solitary nucleus} -> {phrenic nucleus, inspiratory; diaphragm}
-
- TRACT ESS: extensor somatic system; control extensor muscles
-
- TRACT ACST: anterior corticospinal tract (ventral corticospinal tract); extensor motor, pyramidal tract, conscious (premotor BA 6, parietal BA 1,2,3)
-
- TRACT MLFS: medial longitudinal fasciculus system; connects the cranial nerve nuclei III (oculomotor nerve), IV (trochlear nerve) and VI (abducens nerve) together, and integrates movements directed by the gaze centers (frontal eye field) and information about head movement (from cranial nerve VIII, vestibulocochlear nerve) (connects together III, IV, and VI; integral component of saccadic eye movements as well as vestibulo-ocular and optokinetic reflexes; tectospinal and vestibulospinal); path: {vestibular nucleus} -> {}
- TRACT TCST: tectospinal tract; mediate reflex postural movements of head in response to visual and auditory stimuli (extrapyramidal; in response to bright and sudden movements and loud noises)
-
- TRACT VST: vestibulospinal tract; alter muscle tone, extend, and change position of limbs and head with goal of supporting posture and maintaining balance of body and head; maintain balance and to stabilize the visual image on the retina during head movements (extrapyramidal; proximal muscles, postural control; activates extensors, inhibits flexors; vestibular nuclei receive their primary input from the vestibular portion of C.N. VIII - vestibular-auditory)
-

- TRACT LVST: lateral vestibulospinal tract; maintain an upright and balanced posture by stimulating extensor motor neurons in legs (also innervates muscles of the trunk, thus additionally aiding in body posture; lateral vestibular nuclei receive input from cerebellum); path: {lateral vestibular nucleus; additional input from superior and inferior vestibular nuclei} -> {extensor muscles of legs}
-
- TRACT MVST: medial vestibulospinal tract; controls position of the head, neck, and eyes in response to changes in posture (controlling lower motor neurons associated with the spinal accessory nerve - CN XI; additionally, projects superiorly to the paramedian pontine reticular formation, indirectly innervating the nuclei of CN VI and III); path: {medial vestibular nucleus} -> {spinal accessory nucleus, paramedian pontine reticular formation}
-
-
- TRACT TCST: tectospinal tract; mediate reflex postural movements of head in response to visual and auditory stimuli (extrapyramidal; in response to bright and sudden movements and loud noises)
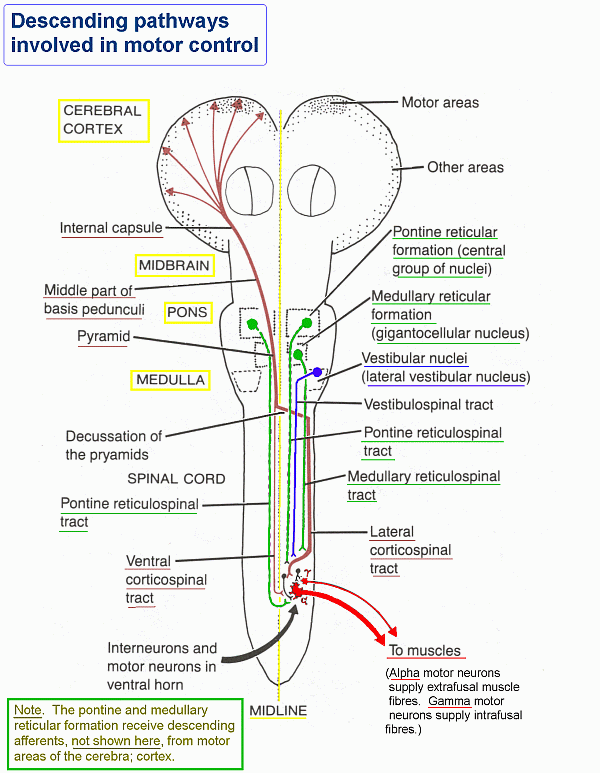
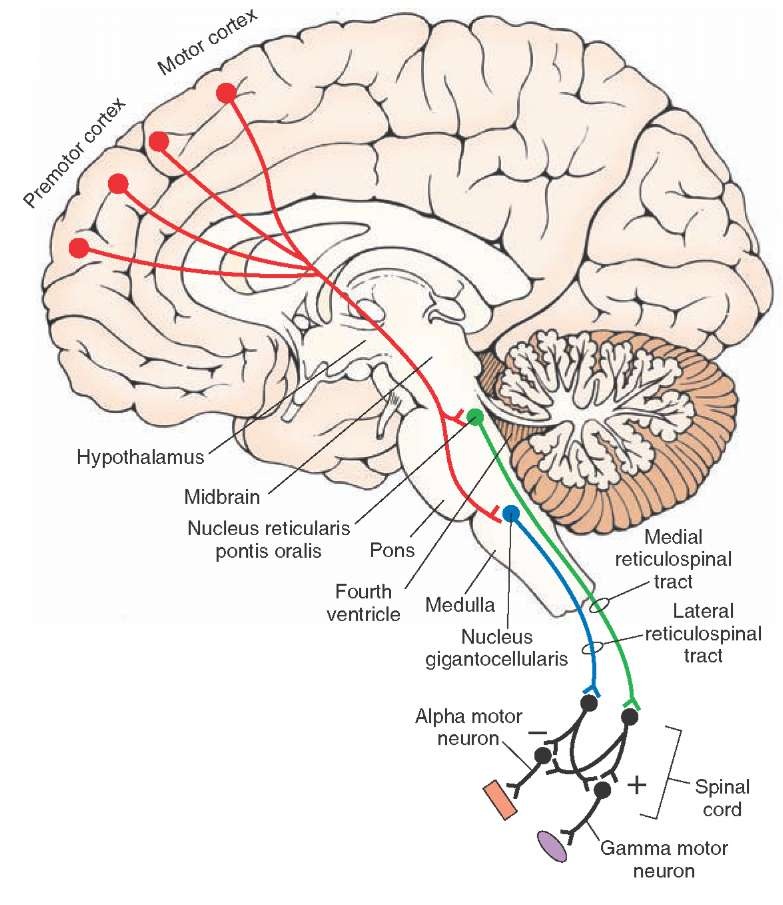
- TRACT RTSS: reticulospinal system; locomotion and postural control (extrapyramidal; proximal muscles, postural control; integrates information from the motor systems to coordinate automatic movements of locomotion and posture; facilitates and inhibits voluntary movement; influences muscle tone; mediates autonomic functions; modulates pain impulses; influences blood flow to lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus)
-
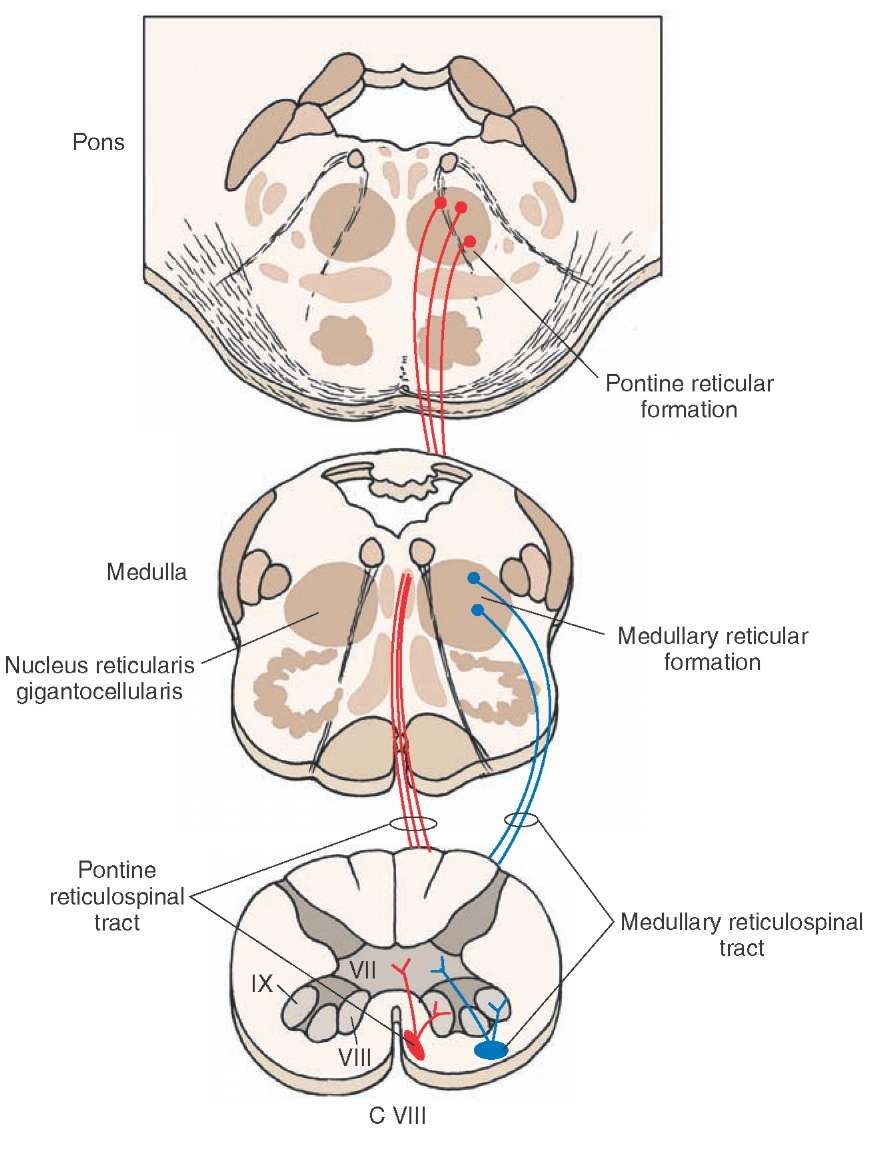
- TRACT MRST: medullary reticulospinal tract (lateral reticulospinal tract); inhibiting excitatory axial extensor muscles of movement; path: {Gigantocellular Reticular Nucleus} -> {extensor muscles}
-
- TRACT PRST: pontine reticulospinal tract (medial reticulospinal tract); exciting anti-gravity, extensor muscles; path: {Oral Pontine Reticular Nucleus} -> {extensor muscles}
-
- TRACT FSS: flexor somatic system; control flexor muscles
-
- TRACT BSS: corticobulbospinal system; pattern locomotion, inhibit reflex activity in spinal cord
- TRACT CBT: corticobulbar tract; carrying the motor function of the non-oculomotor cranial nerves (V, VII, XI, and XII; indirectly - via IX and X in nucleus ambiguus)
-
- TRACT RBST: rubrospinal tract; mediation of voluntary movement, upper limbs; control of flexor tone (extrapyramidal; activates flexors, inhibits extensors)
-
- TRACT CBT: corticobulbar tract; carrying the motor function of the non-oculomotor cranial nerves (V, VII, XI, and XII; indirectly - via IX and X in nucleus ambiguus)
- TRACT ASTT: lateral corticospinal tract; flexor motor, pyramidal tract, conscious; volitional skilled motor activity (90 percents of corticospinal fibers; 80 percents - contrallateral; 10 percents - unilateral; cervical-medial, thoracic, lumbar-lateral, distal muscles, decussating to contralateral and ipsilateral); path: {cortex BA 1-4,6} -> {muscle groups that require concentration and conscious thought to control; upper limb digits}
-